As a Novel Tumor Suppressor, LHPP Promotes Apoptosis by Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 35002505
- PMCID: PMC8741864
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.66841
As a Novel Tumor Suppressor, LHPP Promotes Apoptosis by Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
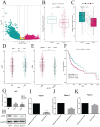
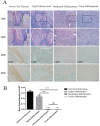
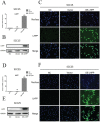
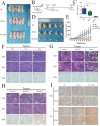
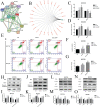
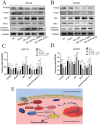
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) refers to the malignant tumor of the head and neck with a highest morbidity. It exhibits a poor prognosis and unsatisfactory treatment partially attributed to delayed diagnosis. As indicated from existing reports, the protein histidine phosphatase LHPP acts as a vital factor in tumorigenesis in liver, lung, bladder, breast and pancreatic tumor tissues. Thus far, the functional mechanism of LHPP in OSCC remains unclear. DGE analysis, OSCC cell lines and OSCC cases were found that LHPP was down-regulated in OSCC tissues and cells compared with that in normal oral mucosa tissues and cells, and was closely related to OSCC differentiation. Cell counting Kit 8 test, EdU proliferation test, scratches test, invasion test, monoclonal formation test, mouse xenograft tumor model, HE staining and immunohistochemistry showed that LHPP inhibited OSCC growth, proliferation and migration in vivo and in vitro. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis, LHPP transcription factor analysis and flow cytometry found that LHPP promotes the apoptosis of OSCC by decreasing the transcriptional activity of p-PI3K and p-Akt. Finally, our results suggested that LHPP inhibited the progression of OSCC through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, indicating that LHPP may be a new target for the treatment of OSCC.
Keywords: LHPP; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; PI3K/AKT pathway; apoptosis; proliferation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LHPP suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion and promotes apoptosis in pancreatic cancer.Biosci Rep. 2020 Mar 27;40(3):BSR20194142. doi: 10.1042/BSR20194142. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32186702 Free PMC article.
-
BCAT1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Dis. 2025 Feb;31(2):364-375. doi: 10.1111/odi.15084. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Oral Dis. 2025. PMID: 39056279
-
Elevated Expression of Zinc Finger Protein 703 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Metastasis through PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β Signalling in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(3):920-934. doi: 10.1159/000485360. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. Retraction in: Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021;55(1):138. doi: 10.33594/000000347. PMID: 29176314 Retracted.
-
Unveiling the nexus: Long non-coding RNAs and the PI3K/Akt pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Oct;262:155540. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155540. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39142241 Review.
-
PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway Mediated Autophagy in Oral Carcinoma - A Comprehensive Review.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Apr 29;21(6):1165-1175. doi: 10.7150/ijms.94566. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38774756 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitation of phosphohistidine in proteins in a mammalian cell line by 31P NMR.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 1;17(9):e0273797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273797. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36048825 Free PMC article.
-
Critical roles and clinical perspectives of RNA methylation in cancer.MedComm (2020). 2024 May 7;5(5):e559. doi: 10.1002/mco2.559. eCollection 2024 May. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38721006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulated PI3K/AKT signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma: The tumor microenvironment and epigenetic modifiers as key drivers.Oncol Res. 2025 Jul 18;33(8):1835-1860. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.064010. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40746882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncolytic adenovirus encoding LHPP exerts potent antitumor effect in lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 7;14(1):13108. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63325-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38849383 Free PMC article.
-
Colitis Is Associated with Loss of the Histidine Phosphatase LHPP and Upregulation of Histidine Phosphorylation in Intestinal Epithelial Cells.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 1;11(8):2158. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082158. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2018;68:7–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

