Underlying the Mechanisms of Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity: Oxidative Stress and Cell Death
- PMID: 35002523
- PMCID: PMC8741835
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.65258
Underlying the Mechanisms of Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity: Oxidative Stress and Cell Death
Abstract
Cancer is a destructive disease that causes high levels of morbidity and mortality. Doxorubicin (DOX) is a highly efficient antineoplastic chemotherapeutic drug, but its use places survivors at risk for cardiotoxicity. Many studies have demonstrated that multiple factors are involved in DOX-induced acute cardiotoxicity. Among them, oxidative stress and cell death predominate. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the mechanisms underlying the source and effect of free radicals and dependent cell death pathways induced by DOX. Hence, we attempt to explain the cellular mechanisms of oxidative stress and cell death that elicit acute cardiotoxicity and provide new insights for researchers to discover potential therapeutic strategies to prevent or reverse doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.
Keywords: Doxorubicin; cardiotoxicity; cell death; oxidative stress.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
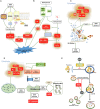
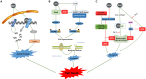
References
-
- Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM, Jemal A. Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates and Trends-An Update. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2016;25:16–27. - PubMed
-
- Shelburne N, Simonds NI, Adhikari B, Alley M, Desvigne-Nickens P, Dimond E. et al. Changing Hearts and Minds: Improving Outcomes in Cancer Treatment-Related Cardiotoxicity. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019;21:9. - PubMed
-
- Von Hoff DD, Layard MW, Basa P, Davis HL Jr, Von Hoff AL, Rozencweig M. et al. Risk factors for doxorubicin-induced congestive heart failure. Ann Intern Med. 1979;91:710–7. - PubMed
-
- Lefrak EA, Pitha J, Rosenheim S, Gottlieb JA. A clinicopathologic analysis of adriamycin cardiotoxicity. Cancer. 1973;32:302–14. - PubMed
-
- Tomita S, Ishida M, Nakatani T, Fukuhara S, Hisashi Y, Ohtsu Y. et al. Bone marrow is a source of regenerated cardiomyocytes in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances migration of bone marrow cells and attenuates cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin under electron microscopy. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2004;23:577–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

