Inhaled Budesonide in Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome of Near-Term Neonates: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35002557
- PMCID: PMC8717620
- DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-27.1.38
Inhaled Budesonide in Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome of Near-Term Neonates: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluates the value of inhaled budesonide (BUD) administration in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) cases especially for near-term neonates.
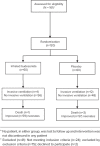
Methods: A randomized controlled trial involving 120 neonates with respiratory distress, which was diagnosed as RDS, was conducted from July 2016 to March 2018. The neonates studied were divided into 2 groups: group 1 (the inhaled BUD group), consisting of 60 neonates who received BUD (2 mL, 0.25-mg/mL suspension) inhalation, twice daily for 5 days; and group 2 (the placebo group), consisting of 60 neonates with RDS who received humidified distilled sterile water inhalation (2 mL). Downes score, RDS grades, and interleukin 8 (IL-8) levels were monitored and measured on the first and fifth days of incubation.
Results: Statistically significant differences (SSDs) in RDS grades, Downes score, and IL-8 levels on the fifth day of admission were observed between groups 1 and 2 (p = 0.001) and between the first and fifth days of incubation in group 1 (p = 0.001). The SSDs in the duration of hospitalization (p = 0.001) and the number of neonates receiving mechanical ventilation (p = 0.032) were found between both groups.
Conclusions: Budesonide inhalation is associated with improvements in clinical and laboratory parameters in neonates with RDS.
Keywords: budesonide; inhaled; neonate; respiratory distress; therapeutic.
Copyright. Pediatric Pharmacy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, email: mhelms@pediatricpharmacy.org 2022.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Adjuvant Therapy with Zinc Supplementation in Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(12):2253-2259. doi: 10.2174/1871530321666210729113515. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 34325645 Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic effect of inhaled budesonide in transient tachypnea of newborn: A placebo-controlled study.J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 5;27(2):e78-e86. doi: 10.15586/jptcp.v27i2.663. J Popul Ther Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32543161 Clinical Trial.
-
[Retrospective analysis of elective caesarean section and respiratory distress syndrome in the term neonates].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Sep;47(9):658-61. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 20021786 Chinese.
-
Inhalation or instillation of steroids for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Neonatology. 2015;107(4):358-9. doi: 10.1159/000381132. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Neonatology. 2015. PMID: 26044104 Review.
-
Budesonide inhalation suspension: a review of its use in infants, children and adults with inflammatory respiratory disorders.Drugs. 2000 Nov;60(5):1141-78. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200060050-00010. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 11129126 Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of the efficacy of budesonide and ambroxol hydrochloride inhalation in children with pneumonia and their effects on inflammatory response.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 19;9(11):e21105. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21105. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37954384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ye W, Zhang T, Shu Y et al. The influence factors of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome in Southern China: a case-control study. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med . 2020;33(10):1678–1682. - PubMed
-
- Kothe TB, Sadiq FH, Burleyson N et al. Surfactant and budesonide for respiratory distress syndrome: an observational study. Pediatr Res . 2020;87(5):940–945. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources