Novel Opipramol-Baclofen Combination Alleviates Depression and Craving and Facilitates Recovery From Substance Use Disorder-An Animal Model and a Human Study
- PMID: 35002647
- PMCID: PMC8733380
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.788708
Novel Opipramol-Baclofen Combination Alleviates Depression and Craving and Facilitates Recovery From Substance Use Disorder-An Animal Model and a Human Study
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Novel Opipramol-Baclofen Combination Alleviates Depression and Craving and Facilitates Recovery From Substance Use Disorder-An Animal Model and a Human Study.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jun 10;16:952004. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.952004. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35755408 Free PMC article.
Abstract
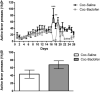
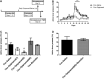
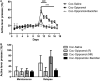
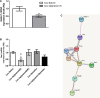
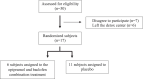
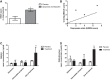
Substance use disorders (SUDs) are associated with depression and anxiety, with the latter being one of the major factors in substance-seeking and relapse. Due to dose-dependent sedative side effects there is limited efficacy of baclofen treatment for SUDs. Here we suggest the use of a novel combination of opipramol and baclofen (O/B) which is known to attenuate anxiety and depression, for the facilitation of recovery from SUDs. Since both opipramol and baclofen have a common downstream signal transduction, their individual doses could be reduced while still maintaining the benefits of the combination. We tested the O/B combination in both animals and patients. Rats treated with O/B showed significant attenuation in craving behavior and in relapse rate during withdrawal from cocaine. In a double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study, conducted in a residential detoxification center, 14 males and 3 females, aged 28-60 years were assigned to a study (n = 6) and a placebo (n = 11) group (placebo group: 40 ± 10.5 years; O/B group 40 ± 10.8 years). The participants completed scales measuring depression, anxiety and craving symptoms and provided saliva samples for stress hormone examination [cortisol and dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate (DHEA-S)]. Participants with polysubstance use disorder (PsUD) treated with O/B showed a reduction in cravings and depression and an increase in DHEA-S and in the DHEA-S/cortisol ratio. Our findings indicate a beneficial effect of O/B treatment. This study suggests a novel candidate for pharmacological treatment of patients with SUD and comorbid mood/anxiety disorders that may facilitate their rehabilitation.
Keywords: addiction; baclofen; opipramol; stress; substance-induced depressive disorder; therapeutic center; treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Bareli, Ahdoot, Ben Moshe, Barnea, Warhaftig, Gispan, Maayan, Rosca, Weizman and Yadid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmadi-Abhari S. A., Akhondzadeh S., Assadi S. M., Shabestari O. L., Farzanehgan Z. M., Kamlipour A. (2001). Baclofen versus clonidine in the treatment of opiates withdrawal, side-effects aspect: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 26 67–71. 10.1046/j.1365-2710.2001.00325.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

