Inhibition of Brain GTP Cyclohydrolase I Attenuates 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Striatal Toxicity: Involvement of Mas Receptor/PI3k/Akt/CREB/ BDNF Axis
- PMID: 35002694
- PMCID: PMC8727546
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.740966
Inhibition of Brain GTP Cyclohydrolase I Attenuates 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Striatal Toxicity: Involvement of Mas Receptor/PI3k/Akt/CREB/ BDNF Axis
Abstract
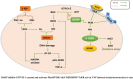
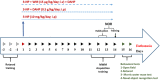
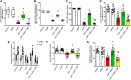
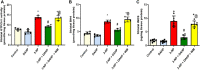
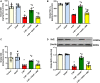
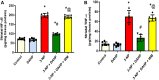
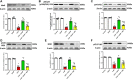
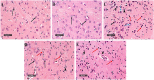
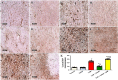
GTP cyclohydrolase I (GTPCH I) is the rate-limiting enzyme for tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) biosynthesis; the latter is an essential factor for iNOS activation that contributes neuronal loss in Huntington's disease (HD). The aim of the study was to investigate the neuroprotective effect of 2,4-diamino-6-hydroxypyrimidine (DAHP), GTPCH I enzyme inhibitor, against neuronal loss in 3-nitropropinic acid (3-NP)-induced HD in rats and to reveal the possible involved mechanisms mediated through PI3K/Akt axis and its correlation to Mas receptor (MasR). Rats received 3-NP (10 mg/kg/day; i.p.) with or without administration of DAHP (0.5 g/kg/day; i.p.) or wortmannin (WM), a PI3K inhibitor, (15 μg/kg/day; i.v.) for 14 days. DAHP improved cognitive, memory, and motor abnormalities induced by 3-NP, as confirmed by striatal histopathological specimens and immunohistochemical examination of GFAP. Moreover, DAHP treatment inhibited GTPCH I activity, resulting in decreased BH4 levels and iNOS activation. Also, DAHP upregulated the protein expression of survival protein; p85/p55 (pY458/199)-PI3K and pS473-Akt that, in turn, boosted the activation of striatal neurotrophic factors and receptor, pS133-CREB, BDNF and pY515-TrKB, which positively affect MasR protein expression and improve mitochondrial dysfunction, as indicated by enhancing both SDH and PGC-1α levels. Indeed, DAHP attenuates oxidative stress by increasing SOD activity and Nrf2 expression in addition to reducing neuro-inflammatory status by inhibiting NF-κB p65 and TNF-α expression. Interestingly, all the previous effects were blocked by co-administration of WM with DAHP. In conclusion, DAHP exerts neuroprotective effect against neuronal loss induced by 3-NP administration via inhibition of GTPCH I and iNOS activity and activation of MasR/PI3K/Akt/CREB/BDNF/TrKB axis besides its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect.
Keywords: 3-nitropropionic acid; DAHP 3; PI3K/AKT signaling; mas receptor; mitochondrial dysfunction.
Copyright © 2021 Mustafa, Rabie, Zaki and Shaheen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vildagliptin Attenuates Huntington's Disease through Activation of GLP-1 Receptor/PI3K/Akt/BDNF Pathway in 3-Nitropropionic Acid Rat Model.Neurotherapeutics. 2020 Jan;17(1):252-268. doi: 10.1007/s13311-019-00805-5. Neurotherapeutics. 2020. PMID: 31728850 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A1 receptor agonist, N6-cyclohexyladenosine, attenuates Huntington's disease via stimulation of TrKB/PI3K/Akt/CREB/BDNF pathway in 3-nitropropionic acid rat model.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Jan 5;369:110288. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110288. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 36509115
-
GTP cyclohydrolase I inhibition by the prototypic inhibitor 2, 4-diamino-6-hydroxypyrimidine. Mechanisms and unanticipated role of GTP cyclohydrolase I feedback regulatory protein.J Biol Chem. 1998 Aug 14;273(33):21091-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.33.21091. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9694862
-
GCH1 variants, tetrahydrobiopterin and their effects on pain sensitivity.Scand J Pain. 2014 Apr 1;5(2):121-128. doi: 10.1016/j.sjpain.2013.12.001. Scand J Pain. 2014. PMID: 29913682 Review.
-
Neuroprotective mechanisms of brain-derived neurotrophic factor against 3-nitropropionic acid toxicity: therapeutic implications for Huntington's disease.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jul;1201:8-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05628.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20649532 Review.
Cited by
-
Europinidin Mitigates 3-NPA-Induced Huntington's Disease Symptoms in Rats: A Comprehensive Analysis of Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Enzyme Complex Activity, Pro-Inflammatory Markers and Neurotransmitter Alterations.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 12;12(3):625. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030625. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540238 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Defenses in Huntington's Disease: Roles of NRF2 and PGC-1α, and Therapeutic Strategies.Life (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;15(4):577. doi: 10.3390/life15040577. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parthenolide ameliorates 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington's disease-like aberrations via modulating NLRP3 inflammasome, reducing microglial activation and inducing astrocyte shifting.Mol Med. 2024 Sep 26;30(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00917-5. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39327568 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Pinene Ameliorates Memory Deficits in 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Rat Model of Huntington's Disease.Neurochem Res. 2025 Apr 16;50(3):144. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04393-z. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40237934
-
Mechanistic insights on the role of Nrf-2 signalling in Huntington's disease.Neurol Sci. 2025 Feb;46(2):593-604. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07802-3. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39392523 Review.
References
-
- Ahmed L. A., Darwish H. A., Abdelsalam R. M., Amin H. A. (2016). Role of Rho Kinase Inhibition in the Protective Effect of Fasudil and Simvastatin against 3-nitropropionic Acid-Induced Striatal Neurodegeneration and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 53, 3927–3938. 10.1007/s12035-015-9303-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arnt J., Bang-Andersen B., Grayson B., Bymaster F. P., Cohen M. P., DeLapp N. W., et al. (2010). Lu AE58054, a 5-HT6 Antagonist, Reverses Cognitive Impairment Induced by Subchronic Phencyclidine in a Novel Object Recognition Test in Rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 13, 1021–1033. 10.1017/S1461145710000659 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

