Phrase Depicting Immoral Behavior Dilates Its Subjective Time Judgment
- PMID: 35002873
- PMCID: PMC8739786
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.784752
Phrase Depicting Immoral Behavior Dilates Its Subjective Time Judgment
Abstract
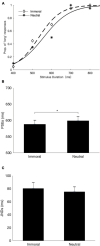
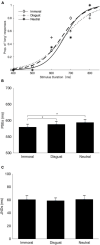
Intuitive moral emotions play a major role in forming our opinions and moral decisions. However, it is not yet known how we perceive the subjective time of moral-related information. In this study, we compared subjective durations of phrases depicting immoral, disgust, or neutral behaviors in a duration bisection task and found that phrases depicting immoral behavior were perceived as lasting longer than the neutral and disgusting phrases. By contrast, the subjective duration of the disgusting phrase, unlike the immoral phrase, was comparable to the neutral phrase. Moreover, the lengthening effect of the immoral phrase relative to the neutral phrase was significantly correlated to the anonymously prosocial tendency of the observer. Our findings suggest that immoral phrases induce embodied moral reaction, which alters emotional state and subsequently lengthens subjective time.
Keywords: disgust phrases; embodied timing; emotion; immoral phrases; time perception.
Copyright © 2021 Jia, Shao, Wang and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Angrilli A., Cherubini P., Pavese A., Manfredini S. (1997). The influence of affective factors on time perception. Percept. Psychophys. 59 972–982. - PubMed
-
- Carlo G., Randall B. A. (2002). The development of a measure of prosocial behaviors for late adolescents. J. Youth Adolesc. 31 31–44. 10.1023/A:1014033032440 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

