Unmet Needs for Rehabilitative Management in Common Health-Related Problems Negatively Impact the Quality of Life of Community-Dwelling Stroke Survivors
- PMID: 35002922
- PMCID: PMC8733320
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.758536
Unmet Needs for Rehabilitative Management in Common Health-Related Problems Negatively Impact the Quality of Life of Community-Dwelling Stroke Survivors
Abstract
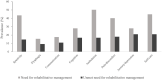
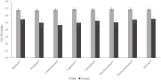
Purpose: Community-dwelling stroke survivors have various unmet needs for rehabilitative management, but there is a lack of in-depth investigations on common health problems after stroke. Moreover, the association between unmet needs and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) has not been thoroughly investigated. This study aimed to investigate the unmet needs for rehabilitative management in common problems after stroke and their associations with HRQoL among community-dwelling stroke survivors. Methods: A face-to-face cross-sectional survey was conducted among community-dwelling stroke survivors visiting outpatient clinics of rehabilitation departments between June and October 2020 in three university-affiliated hospitals. Unmet needs for common problems after stroke were assessed across eight domains based on the post-stroke checklist: spasticity, dysphagia, communication, cognition, ambulation, pain/discomfort, anxiety/depression, and self-care. HRQoL was measured using the EuroQoL-5D three level (EQ-5D). The prevalence of unmet needs for rehabilitative management and their associations with the EQ-5D index were analyzed. Results: Among the 239 participants who responded to the survey, 63% (n = 150) were men. The mean age was 63 ± 13 years, and the mean duration of stroke onset was 55.6 months. Overall, 49% reported at least one unmet need, and the most frequently reported unmet needs were anxiety/depression (20.9%), self-care (20.9%), and pain/discomfort (18.0%). The highest proportion of unmet needs was in the anxiety/depression, communication, and cognition domains. Patients with unmet needs for cognition and pain/discomfort showed a significantly lower EQ-5D index, even after adjusting for age, sex, and modified Rankin scale scores. The total number of unmet needs was significantly correlated with a lower EQ-5D index (Pearson's r = -0.329, p < 0.001) in the multivariate linear regression model. Conclusions: Unmet rehabilitative needs are prevalent among community-dwelling stroke survivors, and the proportion of unmet needs was high among non-physical domains such as anxiety/depression. The number of unmet needs is an independent negative predictor of HRQoL. Systematic approaches to identify unmet needs and provide appropriate rehabilitative management are required in long-term stroke survivors.
Keywords: community-dwelling; post-stroke checklist; quality of life; rehabilitation; stroke; transitional care; unmet need.
Copyright © 2021 Kim, Chang, Jung, Jee, Sohn, Ko, Shin, Leigh, Kim and Paik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

