Gut-Lung Crosstalk in Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury
- PMID: 35003009
- PMCID: PMC8733643
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.779620
Gut-Lung Crosstalk in Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
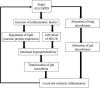
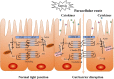
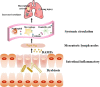
Acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are common acute and severe cases of the respiratory system with complicated pathogenesis and high mortality. Sepsis is the leading indirect cause of ALI/ARDS in the intensive care unit (ICU). The pathogenesis of septic ALI/ARDS is complex and multifactorial. In the development of sepsis, the disruption of the intestinal barrier function, the alteration of gut microbiota, and the translocation of the intestinal microbiome can lead to systemic and local inflammatory responses, which further alter the immune homeostasis in the systemic environment. Disruption of homeostasis may promote and propagate septic ALI/ARDS. In turn, when ALI occurs, elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines and the shift of the lung microbiome may lead to the dysregulation of the intestinal microbiome and the disruption of the intestinal mucosal barrier. Thus, the interaction between the lung and the gut can initiate and potentiate sepsis-induced ALI/ARDS. The gut-lung crosstalk may be a promising potential target for intervention. This article reviews the underlying mechanism of gut-lung crosstalk in septic ALI/ARDS.
Keywords: acute lung injury; gut microbiome; gut-lung crosstalk; inflammation; sepsis.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou and Liao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Agudelo-Ochoa G. M., Valdés-Duque B. E., Giraldo-Giraldo N. A., Jaillier-Ramírez A. M., Giraldo-Villa A., Acevedo-Castaño I., et al. (2020). Gut microbiota profiles in critically ill patients, potential biomarkers and risk variables for sepsis. Gut Microbes 12:1707610. 10.1080/19490976.2019.1707610 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

