Duck Plague Virus pUL48 Protein Activates the Immediate-Early Gene to Initiate the Transcription of the Virus Gene
- PMID: 35003026
- PMCID: PMC8733724
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.795730
Duck Plague Virus pUL48 Protein Activates the Immediate-Early Gene to Initiate the Transcription of the Virus Gene
Abstract
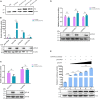
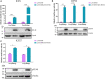
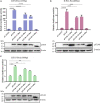
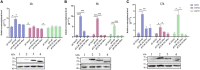
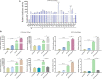
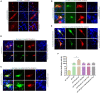
Duck plague caused by the duck plague virus (DPV) is an infectious disease that seriously harms the waterfowl breeding industry. The VP16 protein of α herpesvirus can bind to specific cis-acting elements upstream of the promoter of the immediate-early (IE, α) gene to promote the transcription of the IE gene, so it is also called the trans-inducer of IE gene (α-TIF). However, no studies on DPV α-TIF have been reported. This study investigated the DPV pUL48, a homolog of HSV-1 VP16, transcriptional activation region, target sequence, and viral protein affecting its transcriptional activation using a dual-luciferase reporter gene detection system, and pUL48 was identified as the α-TIF of DPV. (1) The regulation of pUL48 on DPV different gene promoters showed that pUL48 could activate all the promoters of IE genes (ICP4, ICP22, and ICP27) but not the promoters of early and late genes. (2) The activity of pUL48 to ICP4 and ICP22 promoters with different upstream lengths showed that pUL48 activated ICP4 and ICP22 promoters by acting on TAATGA (T) TAT element upstream of ICP4 promoter and TAATTATAT element upstream of ICP22 promoter, respectively. (3) Transcriptional activation of IE gene by truncated proteins of different lengths at the N-terminal of pUL48 was detected. The results showed that the transcriptional activation domain of pUL48 was amino acids 1-60 at the N-terminal, and amino acids 1-20 was its core region. In addition, it was found that pUL14, pUL46, and pUL47 significantly promoted the transcriptional activation of pUL48. The effects of loss of pUL47 and its nuclear localization signal on the nuclear entry and transcriptional activation function of pUL48 were further examined. The results showed that pUL47 could promote the nuclear entry of pUL48 through its nuclear localization signal at positions 40-50 and 768-777 amino acids, thus, enhancing the transcriptional activation function of pUL48 and synergistic promotion of viral gene transcription.
Keywords: duck plague virus; immediate early genes; pUL48; transcriptional activation domain; transcriptional activation function.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Fan, Wang, Cheng, Wu, Yang, Tian, Jia, Ou, Mao, Sun, Zhang, Zhu, Chen, Liu, Zhao, Huang, Gao, Yu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification and subcellular localization of proteins that interact with Duck plague virus pUL14 in infected host cells.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104649. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104649. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39675104 Free PMC article.
-
Duck plague virus Us3 regulates the expression of pUL48.Poult Sci. 2024 Apr;103(4):103498. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103498. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38364609 Free PMC article.
-
Research Note: Duck plague virus pUL48 is a late protein that plays an important role in viral replication.Poult Sci. 2023 Feb;102(2):102358. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102358. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 36473386 Free PMC article.
-
A Revision of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Transcription: First, Repress; Then, Express.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 26;12(2):262. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020262. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herpesvirus Late Gene Expression: A Viral-Specific Pre-initiation Complex Is Key.Front Microbiol. 2016 Jun 6;7:869. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00869. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27375590 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple functions of the herpesvirus UL14 gene product in viral infection.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 23;15:1483022. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1483022. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39507342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and subcellular localization of proteins that interact with Duck plague virus pUL14 in infected host cells.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104649. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104649. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39675104 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Double Copies of the US1 Gene Reduces the Infectivity of Recombinant Duck Plague Virus In Vitro and In Vivo.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0114022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01140-22. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36377937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar X., Blomberg J., Brännström K., Olofsson A., Schleucher J., Björklund S. (2014). Interaction studies of the human and Arabidopsis thaliana Med25-ACID proteins with the herpes simplex virus VP16- and plant-specific Dreb2a transcription factors. PLoS One 9:e98575. 10.1371/journal.pone.0098575 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara S., Kigoshi K., Mitsuda N., Suzuki K., Ohme-Takagi M. (2014). VP16 fusion efficiently reveals the function of transcriptional repressors in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol. 31 123–132. 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.14.0121a - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

