Bioactive Nutrient Fortified Fertilizer: A Novel Hybrid Approach for the Enrichment of Wheat Grains With Zinc
- PMID: 35003150
- PMCID: PMC8733721
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.743378
Bioactive Nutrient Fortified Fertilizer: A Novel Hybrid Approach for the Enrichment of Wheat Grains With Zinc
Abstract
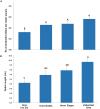
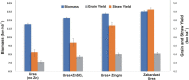
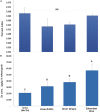
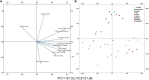
Zinc (Zn) is a critical micronutrient that synergizes nutrient use efficiency, and improves plant growth and human health. Low Zn bioavailability in soils affects produce quality and agricultural productivity worldwide ultimately inducing deficiency in humans and animals. Zn deficiency is a leading cause of malnutrition in underdeveloped countries where a widespread population depends upon staple cereals for daily intake of calories. Modern cereal cultivars are inherently low in Zn, eventually, plants need to be enriched with soil application of ZnSO4, but due to higher fixation losses, it becomes an inefficient source. Rhizosphere microbiome contains Zn-solubilizing bacteria (ZSB) that improve Zn bioavailability, thus increase the root function, Zn uptake, and plant growth. Niha Corp developed a hybrid process of bioactive nutrient fortified fertilizer (BNFF), which has been used to formulate Zabardast Urea (ZU) by coating bioactive Zn (BAZ) and ZSB on urea. Data obtained for 15 wheat varieties from 119 farmer field demonstration plots and eight replicated trials on 42 locations across multi-environment conditions conclude that ZU significantly improved the plant biomass and yield by 12% over non-Zn control and produced grains with 57 μg/g Zn contents, which can meet a major part of the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) of humans. The study recommends that this microbe-mediated hybrid invention (ZU) is a feasible approach to boost Zn bioavailability and Zn use efficiency, with enhanced yield and quality that may contribute to improve human health. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first wide-scale field testing of Zn enrichment in the grains of bread wheat using an innovative BNFF Urea Z technology.
Keywords: Zn solubilizing bacteria; agriculture productivity; bio-fortified nutrient fertilizer; plant-growth; rhizosphere; zinc-biofortification.
Copyright © 2021 Ali, Naeem, Tariq, Ahmed and Imran.
Conflict of interest statement
MA and IA were employed by Engro Fertilizers Limited. FN and NT were employed by First Biotech LLC, Lahore. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad M., Adil Z., Hussain A., Mumtaz M. Z., Nafees M., Ahmad I., et al. (2019). Potential of phosphate solubilizing Bacillus strains for improving growth and nutrients uptake in mugbean and miaze crops. Pak. J. Agri. Sci. 56 283–289. 10.21162/PAKJAS/19.7285 - DOI
-
- Alloway B. J. (2009). Soil factors associated with zinc deficiency in crops and humans. Environ. Geochem. Health 31 537–548. - PubMed
-
- Anjum A., Yousaf M., Zuber M., Bukhari T. H., Zahoor A. F., Khan Z. I., et al. (2012). A comparative study on the status of Zn and Cu in diabetic and non diabetic males in Punjab, Pakistan. Afr. J. Phar. Pharmacol. 6 1482–1486. 10.5897/AJPP12.252 - DOI
-
- Bhutta Z. A., Jiwani A., Feroze A., Kissana N., Monasterio I. O. (2007). Assessment of human zinc deficiency and determinants in Pakistan: Implications for interventions. Zinc Crops 2007. Improving Crop Production and Human Health, Istanbul, Turkey. Plant Soil 306 1–2.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

