Efficacy and Safety of Acupuncture Combined with Herbal Medicine in Treating Gouty Arthritis: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 35003310
- PMCID: PMC8736704
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8161731
Efficacy and Safety of Acupuncture Combined with Herbal Medicine in Treating Gouty Arthritis: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
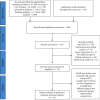
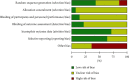
Background: Gouty arthritis is a common metabolic disease caused by long-term purine metabolism and elevated serum uric acid. In recent years, the incidence of gouty arthritis has been increasing year by year. As an effective method for treating gouty arthritis, acupuncture combined with herbal medicine has been widely used in clinical practice. However, the evidence for the treatment needs to be evaluated through systematic review and meta-analysis. Methods. The Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, China CBM database, Clinical Trials, CNKI, China Wanfang database, and VIP information database were searched from the establishment of each database to March 2021. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included in the study, and the therapeutic effects of acupuncture combined with herbal medicine versus conventional therapy, or acupuncture combined with herbal medicine versus anti-inflammatory drugs, or acupuncture combined with herbal medicine versus acupuncture/herbal medicine alone were compared in the subjects with gouty arthritis. Two authors screened all references, assessed the risk of bias, and independently extracted the data. The binary outcome was summarized using 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and risk ratios (RRs). The overall quality of the evidence was assessed with hierarchy, and meta-analysis was performed with a random-effects model.
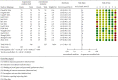
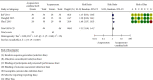
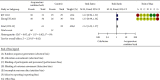
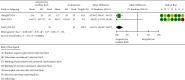
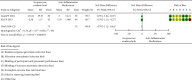
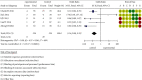
Results: A total of 14 randomized controlled trials (1,065 participants, 540 treatment groups, and 525 control groups) with treatment courses of 5 to 21 days were included. Acupuncture combined with herbal medicine and acupuncture was compared in three trials, acupuncture combined with herbal medicine and conventional therapy was compared in 14 of them, and acupuncture combined with herbal medicine and anti-inflammatory drugs was compared in 8 of them. The clinical efficacy (clinical symptoms, serological tests, and visual analogue scale (VAS) results) was significantly improved in the acupuncture combined with herbal medicine treatment group (P=0.0005, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.13; 687 participants; 8 trials), and the efficacy in reducing uric acid was also better (P < 0.00001; 95% CI -102.89, -68.37; 100 participants; 2 trials; evidence with moderate quality). The effect of acupuncture combined with herbal medicine was better than that of acupuncture alone (RR 1.22, 95%CI 1.06 to 1.41; 139 participants; 3 trials), the effect of acupuncture combined with herbal medicine was better than that of herbal medicine alone (RR 1.31 95%CI 1.08 to 1.57, 100 participants, 2 trials, evidence with moderate quality), and the effect of acupuncture combined with herbal medicine was better than that of colchicine (P = 0.02, RR 1.14 95%CI 1.02 to 1.27, 2 trials, evidence with moderate quality). The incidence of adverse events was considerably different between the two groups, and the acupuncture combined with herbal medicine group was significantly superior to the control group in terms of adverse events (P < 0.00001; 95% CI (0.08 to 0.32)).
Conclusions: The efficacy of acupuncture combined with herbal medicine was better than conventional drug therapy in treating gouty arthritis. The study results must be interpreted with caution due to the high or unclear risk of bias of the trials included in the study. PROSPERO registration number: CRD42020202544. INPLASY registration number: 202090006.
Copyright © 2021 Huan Liang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Iwona S.-S., Diana A. P., Jacobson Jon A. Imaging of gout:findings and pitfalls. A pictorial review. Acta Reumatol Port . 2020;45:20–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

