LATS1 exerts tumor suppressor functions via targeting Gli1 in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 35003351
- PMCID: PMC8734409
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.62211
LATS1 exerts tumor suppressor functions via targeting Gli1 in colorectal cancer
Abstract
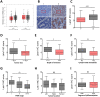
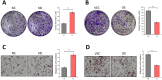
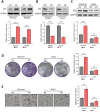
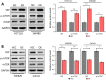
Background: The Hippo pathway's primary kinase component, large tumor suppressor 1 (LATS1), has been hypothesized as a tumor suppressor in a variety of cancers. LATS1's biological effects on colorectal cancer (CRC) are yet to be determined. Methods: The analysis of LATS1 mRNA expression in CRC was conducted using public databases from the Gene Expressing Profiling Interactive Analysis database (GEPIA). Investigation for the expression of LATS1 protein in 102 CRC tumor tissues and 57 normal tissues was performed using immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis. In vitro genetic manipulation was used to explore the potential role and mechanism of LATS1 in the regulation of proliferation and migration of CRC cells. Results: LATS1 was found to be considerably downregulated in CRC tissues, with much lower levels in individuals with bigger tumors of size (≥5 cm), deeper invasion (T3-4), positive lymph node metastasis (LNM), and advanced tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage (III-IV). As exhibited by clinical data analysis, LATS1 loss was significantly associated with TNM and LNM staging in CRC patients. Furthermore, our in vitro investigations revealed that LATS1 depletion increased CRC cell proliferation and migration in HCT116 cells, whereas overexpressing LATS1 had the opposite effect in SW620 cells. LATS1 suppressed the expression of glioma-associated oncogene-1 (Gli1), and LATS1's tumor-suppressive actions in CRC are dependent on Gli1. Moreover, LATS1 could modulate Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) expression and mTOR activation in CRC cells. Conclusion: Our findings identify the LATS1 as a unique Gli1 regulator in CRC cell migration and proliferation, and suggest that LATS1 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for CRC.
Keywords: Gli1; LATS1; colorectal cancer; migration; proliferation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
AIM2 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and migration through suppression of Gli1.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Dec 3;13(1):1017-1031. doi: 10.18632/aging.202226. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33291082 Free PMC article.
-
Rab1A promotes cell proliferation and migration by upregulating Gli1 in colorectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 10;11(1):16243. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95798-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34376787 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the tumor‑suppressive role of circular RNA‑FOXO3 in colorectal cancer via regulation of miR‑543/LATS1 axis.Oncol Rep. 2021 Nov;46(5):239. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8190. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34549306 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-590-3p promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer via Hippo pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 22;8(35):58061-58071. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19487. eCollection 2017 Aug 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28938537 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of aberrant expression of GLI1/p-S6K on colorectal cancer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 18;503(4):3198-3204. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.124. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30143258
Cited by
-
Targeting the Hippo Pathway in Gastric Cancer and Other Malignancies in the Digestive System: From Bench to Bedside.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 8;10(10):2512. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102512. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA binding protein RBM22 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis by stabilizing LATS1 mRNA.J Mol Histol. 2024 Nov 29;56(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10285-3. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39612045
-
Comprehensive identification of a migrasomes-associated long non-coding RNA signature to predict the prognosis and treatment options in colon adenocarcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 27;16(1):409. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02197-9. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40146487 Free PMC article.
-
m6A Reader PRRC2A Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression via CK1ε-Mediated Activation of WNT and YAP Signaling Pathways.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jan;12(3):e2406935. doi: 10.1002/advs.202406935. Epub 2024 Nov 24. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39582289 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo signaling pathway in human testis and seminoma: anticancer effect of verteporfin on human seminoma TCam-2 cells.J Mol Histol. 2025 Aug 22;56(5):273. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10565-6. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40844663 No abstract available.
References
-
- N. Keum, E. Giovannucci. Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:713–732. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ, Meester RGS, Barzi A, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:177–193. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

