PD-L1 Expression in Chinese Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Multi-Center Retrospective Observational Study
- PMID: 35003359
- PMCID: PMC8734414
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.63003
PD-L1 Expression in Chinese Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Multi-Center Retrospective Observational Study
Abstract
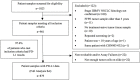
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of tumor programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in Chinese patients with advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Methods: Tumor tissues with histologically confirmed stage IIIB/IV NSCLC were retrospectively obtained from 10 centers in China. PD-L1 expression was determined using the PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and the samples were repetitively assayed with the PD-L1 IHC 22C3 Ab concentrate (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Results: Out of 901 patients who met the inclusion criteria, 879 (97.6%) had evaluable PD-L1 data. The number of patients with a PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) < 1%, 1-49%, and ≥ 50% (corresponding to PD-L1 non-expression, low expression, and high expression) was 424 (48.2%), 266 (30.3%), and 189 (21.5%), respectively. PD-L1 expression was more likely to be found in patients younger than 75 years, men, current or former smokers, those with good performance status (PS) scores, and those with a wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). PD-L1 TPS ≥ 50% and ≥ 1% were respectively 28.0% and 50.2% among patients negative for both EGFR mutation and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangement. PD-L1 expression determined using the 22C3 antibody concentrate and pharmDx kit had comparable results. Conclusions: The prevalence of PD‑L1 expression in advanced NSCLC was consistent with that reported in the global EXPRESS study. Age, gender, smoking history, PS scores, and EGFR/ALK mutation status affected PD-L1 expression. The 22C3 antibody concentrate appears to be an alternative reagent for the PD-L1 assay.
Keywords: 22C3 antibody; driver mutations; immunohistochemistry; non-small cell lung cancer; programmed death-ligand 1.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Anhua Mao, Wenmin Tang, Zhenhua Liu, Jiali Wang and Suijun Xiao are employees of MSD China. Other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD. et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S. et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS) J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2866–74. - PubMed
-
- Mok TSK, Wu YL, Kudaba I. et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393:1819–30. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG. et al. Updated Analysis of KEYNOTE-024: Pembrolizumab Versus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer With PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score of 50% or Greater. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:537–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous