A randomized control trial comparing the efficacy of 3Mixtatin and Modified 3Mix-MP paste using lesion sterilization and tissue repair technique to conventional root canal treatment in primary molars of children aged 4-8 years: An in vivo study
- PMID: 35003558
- PMCID: PMC8672123
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-3327.330874
A randomized control trial comparing the efficacy of 3Mixtatin and Modified 3Mix-MP paste using lesion sterilization and tissue repair technique to conventional root canal treatment in primary molars of children aged 4-8 years: An in vivo study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate clinical and radiographic success rates of 3Mixtatin and Modified 3Mix-MP paste and compare it with conventional root canal treatment procedure in primary molars requiring pulpectomy.
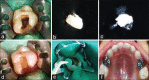
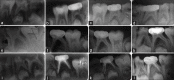
Materials and methods: In this in vivo study, 66 primary molars in 52 children aged between 4 and 8 years with primary molars having chronic periapical abscess were treated randomly with 3Mixtatin, Modified 3Mix-MP paste, and Metapex. The subjects were reviewed at 6 and 12 months both clinically and radiographically after pulpal therapy to evaluate and compare the healing process. The data obtained were subjected to statistical analysis at a significance level of 0.05.
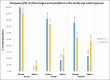
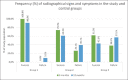
Results: By the end of 12-month follow-up among the three groups, Group I seemed to be performing consistently better as compared to the other two groups when evaluated clinically and radiographically. However, Group III resulted in the greatest number of failures, with success rate being mere 42.9% at the end of follow-up period.
Conclusion: Radiographic and clinical healing occurred in all the three groups; however, based on our results, Group I seemed to be performing consistently better among the three groups at 12-month follow-up. Hence, it can be inferred that 3Mixtatin used as a localized agent is effective and comparable to both Modified 3Mix-MP paste and conventional pulpectomy procedure involving calcium hydroxide and iodoform paste in primary teeth.
Keywords: Metapex; primary teeth; pulpectomy.
Copyright: © 2021 Dental Research Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or non-financial in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of clinical and radiographic success of three different lesion sterilization and tissue repair techniques as treatment options in primary molars requiring pulpectomy: An in vivo study.J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2019 Apr-Jun;37(2):185-191. doi: 10.4103/JISPPD.JISPPD_6_19. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2019. PMID: 31249184
-
In Search of a Novel Substitute: Clinical and Radiological Success of Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair with Modified 3Mix-MP Antibiotic Paste and Conventional Pulpectomy for Primary Molars with Pulp Involvement with 18 Months Follow-up.Contemp Clin Dent. 2017 Oct-Dec;8(4):514-521. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_47_17. Contemp Clin Dent. 2017. PMID: 29326499 Free PMC article.
-
Success of Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair Therapy and Pulpectomy in the Management of Infected Primary Molars with Poor Prognosis.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024 Jan;17(1):41-47. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2750. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2024. PMID: 38559868 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Success Rate of Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair Compared to Vitapex in Pulpally Involved Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review.J Conserv Dent. 2019 Nov-Dec;22(6):510-515. doi: 10.4103/JCD.JCD_76_20. Epub 2020 Aug 20. J Conserv Dent. 2019. PMID: 33088056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Non-Vital Pulp Therapies in Primary Teeth.Pediatr Dent. 2020 Sep 15;42(5):337-349. Pediatr Dent. 2020. PMID: 33087217
Cited by
-
Comparison of 3Mixtatin and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate in Primary Teeth Pulpotomy: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 Jan 11;17(1):e77284. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77284. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39931597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the modified 3Mix-Simvastatin combination in non-instrumental endodontic therapy of necrotic primary molars: A two-arm randomized controlled trial.Clin Exp Dent Res. 2024 Apr;10(2):e860. doi: 10.1002/cre2.860. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2024. PMID: 38433296 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of an antibacterial mixture and non-instrumentation endodontic treatment in primary teeth: A systematic review and meta-analyses.Saudi Dent J. 2023 Sep;35(6):575-588. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2023.06.001. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Saudi Dent J. 2023. PMID: 37823084 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Guideline on pulp therapy for primary and young permanent teeth. Pediatr Dent. 2004;26:115–9. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Guidelines on pulp therapy for primary and young permanent teeth. Reference Manual 2006-07. Pediatr Dent. 2007;28:144–8.
-
- Kher MS, Rao A. Nature Switzerland AG: Springer; 2019. Contemporary Treatment Techniques in Pediatric Dentistry; pp. 75–98.
-
- Ahmed HM. Anatomical challenges, electronic working length determination and current developments in root canal preparation of primary molar teeth. Int Endod J. 2013;46:1011–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
