Indication-based protocols with different solutions for mechanical stromal-cell transfer
- PMID: 35003762
- PMCID: PMC8738882
- DOI: 10.1177/20595131211047830
Indication-based protocols with different solutions for mechanical stromal-cell transfer
Abstract
Background: Regenerative medicine is the fastest developing branch of plastic surgery in recent times. Adipose tissue is one of the largest and most important sources in the body for stromal cells. Although mechanical isolation methods are both very popular and have many advantages, they still have no accepted protocols.
Objective: We developed new protocols called indication-based protocols (IPs) for standardization and new techniques called mechanical stromal-cell transfer (MEST) by using ultra-sharp blades and dilution of adipose tissue with different solutions (saline, Ringer and 5% Dextrose)Methods & material: In order to obtain the desired physical structure (liquid, gel, solid) and the desired volume, four different types of IPs have been defined. Adipose tissue was prediluted with different solutions using 10 or 20 cc injectors in IPs 1 and 2, while condensed adipose tissue was used directly in IPs 3 and 4.
Results: In MEST, stromal cells were obtained from 100 mL of condensed fat using different IPs with 92% mean viability and cell counts of 26.80-91.90 × 106. Stromal cells can be obtained in the desired form and number of cells by using four different IPs.
Conclusion: Isolation of stromal cells by cutting fat with sharp blades will prevent the death of fat tissue and stromal cells and will allow high viability and cell count with our new technique. Predilution with different solutions: Diluting the condensed adipose tissue with the desired solutions (saline, Ringer or 5% Dextrose) before the adinizing process will provide even more stromal cells.
Lay summary: Obtaining regenerative stromal cells from adipose tissue can be done by two methods: Enzymatic and mechanical. Mechanical methods have many advantages. Although mechanical stromal cell extraction from adipose tissue is very popular and many techniques have been described, there are still no accepted protocols, definition for the end product, and no consensus on the status of the stromal cells. In this study, stromal cells were obtained mechanically by using ultra-sharp blade systems, without exposing adipose tissue to blunt trauma. Thus, a higher number of cells and higher viability could be obtained. An "Indication based" protocol has been defined for the first time in order to obtain the desired number and status (solid, semi-solid, liquid)end product. Diluting the condensed adipose tissue with the desired solutions (saline, Ringer or 5% Dextrose) before the adinizing process will provide even more stromal cells. This will provide an opportunity for clinicians to obtain and apply a stromal cell solution for different indications in different anatomical regions.
Keywords: Stromal cells; adipose tissue; cell treatment; mechanical; stromal vascular fraction; total stromal-cells.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


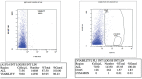


Similar articles
-
A New Classification for Adipose-derived Stromal-cell Systems.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022 Dec 13;10(12):e4712. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004712. eCollection 2022 Dec. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022. PMID: 36583163 Free PMC article.
-
New Mechanical Fat Separation Technique: Adjustable Regenerative Adipose-tissue Transfer (ARAT) and Mechanical Stromal Cell Transfer (MEST).Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2020 Jul 22;2(4):ojaa035. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojaa035. eCollection 2020 Dec. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2020. PMID: 33791661 Free PMC article.
-
Three states of stromal cells-solid, liquid, and aerosol-and innovative delivery methods not previously reported.Arch Plast Surg. 2021 Sep;48(5):549-552. doi: 10.5999/aps.2021.00311. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Arch Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 34583444 Free PMC article.
-
Not Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) or Nanofat, but Total Stromal-Cells (TOST): A New Definition. Systemic Review of Mechanical Stromal-Cell Extraction Techniques.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021 Feb;18(1):25-36. doi: 10.1007/s13770-020-00313-0. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021. PMID: 33231864 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical Fractionation of Adipose Tissue-A Scoping Review of Procedures to Obtain Stromal Vascular Fraction.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Oct 9;10(10):1175. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10101175. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892905 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Evaluation of Mechanically Processed Stromal Vascular Fraction in a Chamber Vascularized by an Arteriovenous Shunt.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 14;14(2):417. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020417. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214149 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding and controlling the variables for stromal vascular fraction therapy.World J Stem Cells. 2024 Aug 26;16(8):784-798. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v16.i8.784. World J Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 39219728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autologous Adipose-Derived Tissue Stromal Vascular Fraction (AD-tSVF) for Knee Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 4;23(21):13517. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113517. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Classification for Adipose-derived Stromal-cell Systems.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022 Dec 13;10(12):e4712. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004712. eCollection 2022 Dec. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022. PMID: 36583163 Free PMC article.
-
Autologization of Exosomes with Deparenchymized Adipose Tissue: An Innovative Approach for Regenerative Medicine and Surgery.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 Jul 16;12(7):e5982. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005982. eCollection 2024 Jul. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 39015362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schildberg FA, Donneberg VS S. Stromal cells in health and disease. Cytometry 2018; 93: 871–875. - PubMed
-
- Alexander RW. Understanding mechanical emulsification (nanofat) versus enzymatic isolation of tissue stromal vascular fraction (tSVF) cells from adipose tissue: potential uses in biocellular regenerative medicine. J Prolother 2016; 8: 947–960.
-
- Guo J, Widgerow AD, Banyard D, et al. Strategic sequences in fat graft survival. Ann Plast Surg 2015; 74: 376–382. - PubMed
-
- Tonnard P, Verpaele A, Peeters G, et al. Nanofat grafting: basic research and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 2013; 132: 1017–1026. - PubMed
-
- Morestin H. Quelques cas de greffes graisseuse appliquees aIa chirurgie reparatrice. Bull Mem Soc Chir (Paris) 1915; 41: 1631.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

