Long COVID Mimicking Interstitial Lung Disease: A Case Series
- PMID: 35003784
- PMCID: PMC8679157
- DOI: 10.12865/CHSJ.47.03.22
Long COVID Mimicking Interstitial Lung Disease: A Case Series
Abstract
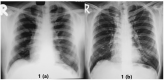
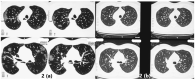
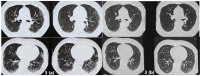
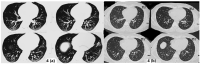
Interstitial lung diseases (ILD) can occur due to various known or unknown causes. They usually present with dry cough and exertional dyspnea. On radiology usual findings are ground glass opacities (GGO's), reticular shadows, nodules etc. Some patients after acute COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) suffer from persistent symptoms/manifestations. These have been called 'Long COVID'. Long COVID also has radiological features like GGO's, nodules and reticulations. Further, patients even without history of acute COVID-19, can also present with 'Long COVID'. In the present case series, we describe three such cases with no history of having suffered from COVID-19, presenting with ILD like features and diagnosed as Long COVID. We infer from these cases that 'Long COVID' can both clinically and radiologically mimic ILD's. Hence, emphasizing the fact that in the present COVID-19 pandemic situation, 'Long COVID should be a differential diagnosis to be considered while making a new diagnosis of ILD.
Keywords: COVID-19 RT-PCR Testing; COVID19; IgG; Interstitial Lung Disease; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2014, Medical University Publishing House Craiova.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures
References
-
- King TE. Clinical Advances in the Diagnosis and Therapy of the Interstitial Lung Diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172(3):268–279. - PubMed
-
- Kreuter M, Herth FJF, Wacker M, Leidl R, Hellmann A, Pfeifer M, Behr J, Witt S, Kauschka D, Mall M, Günther A, Markart P. Exploring Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Interstitial Lung Diseases: Rationale, Aims, and Design of a Nationwide Prospective Registry-The EXCITING-ILD Registry. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:123876–123876. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
