Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor ameliorate hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats
- PMID: 35003786
- PMCID: PMC8684041
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2020-0204
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor ameliorate hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats
Abstract
Objectives: Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD) is a major cause of brain injury in neonates. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) show therapeutic potential for HIBD, and genetic modification may enhance their neuroprotective effects. The goal of this study was to investigate the neuroprotective effects of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-overexpressing BMSCs (BMSCs-HGF) against HIBD and their underlying mechanisms.
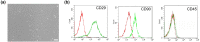
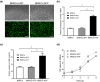
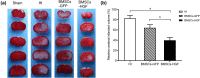
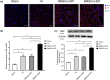
Methods: BMSCs were transfected with HGF using adenoviral vectors. HIBD models were established and then BMSCs were transplanted into the brains of HIBD rats via intraventricular injection. 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining was used to measure cerebral infarction volumes. In vitro, primary cultured cortical neurons were co-cultured with BMSCs in a Transwell plate system. Oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) was applied to imitate hypoxic-ischemic insult, and PD98059 was added to the culture medium to block the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). Cell apoptosis was determined using TUNEL staining. The expression of HGF was measured by immunofluorescence, real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR), and western blots. The expression of phosphorylated ERK (p-ERK) and B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) was measured by western blots.
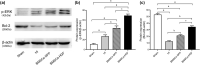
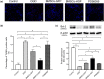
Results: HGF-gene transfection promoted BMSC proliferation. Moreover, BMSCs-HGF decreased HIBD-induced cerebral infarction volumes and enhanced the protective effects of the BMSCs against HIBD. BMSCs-HGF also increased expression of HGF, p-ERK, and Bcl-2 in brain tissues. In vitro, BMSC-HGF protected neurons against OGD-induced apoptosis. Inhibition of ERK phosphorylation abolished the neuroprotective effect of BMSCs-HGF against OGD.
Conclusions: BMSCs-HGF is a potential treatment for HIBD and that the ERK/Bcl-2 pathway is involved in the underlying neuroprotective mechanism.
Keywords: adenoviral vector; bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell; extracellular signal-regulated kinase; hepatocyte growth factor; hypoxic–ischemic brain damage.
© 2021 Wen Zeng et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Finder M, Boylan GB, Twomey D, Ahearne C, Murray DM, Hallberg B. Two-year neurodevelopmental outcomes after mild hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in the era of therapeutic hypothermia. JAMA Pediatr. 2020;174:48–55. - PMC - PubMed
- Finder M, Boylan GB, Twomey D, Ahearne C, Murray DM, Hallberg B. Two-year neurodevelopmental outcomes after mild hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in the era of therapeutic hypothermia. JAMA Pediatr. 2020;174:48–55. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tagin MA, Woolcott CG, Vincer MJ, Whyte RK, Stinson DA. Hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Pediatri Adolesc Med. 2012;166:558–66. - PubMed
- Tagin MA, Woolcott CG, Vincer MJ, Whyte RK, Stinson DA. Hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Pediatri Adolesc Med. 2012;166:558–66. - PubMed
-
- Qin X, Cheng J, Zhong Y, Mahgoub OK, Akter F, Fan Y, et al. Mechanism and treatment related to oxidative stress in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:88. - PMC - PubMed
- Qin X, Cheng J, Zhong Y, Mahgoub OK, Akter F, Fan Y. et al. Mechanism and treatment related to oxidative stress in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:88. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
