A Rare Case of Pseudomembranous Colitis Presenting with Pleural Effusion and Ascites with Literature Review
- PMID: 35003814
- PMCID: PMC8741396
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6019068
A Rare Case of Pseudomembranous Colitis Presenting with Pleural Effusion and Ascites with Literature Review
Abstract
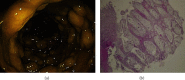
Clostridium difficile infection usually results from long-term and irregular antibiotic intake. The high-risk individuals for this infection include the patients undergoing chemotherapy due to malignancy, immunocompromised patients, and hospitalized patients receiving broad-spectrum antibiotics. The most common clinical manifestation of Clostridium difficile infection is diarrhea. However, pleural effusion and ascites have rarely been observed. As mentioned, these manifestations can be developed in a patient being treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics. Therefore, the present study reports a rare case of Clostridium difficile infection manifesting with these rare manifestations who was a 78-year-old female patient with a history of COVID-19, orthopedic surgery, and antibiotic treatment with cefixime and gentamicin.
Copyright © 2021 Hossain Salehi and Amir Mohammad Salehi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen S. H., Gerding D. N., Johnson S., et al. Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults: 2010 update by the society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the infectious diseases society of America (IDSA) Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology . 2010;31(5):431–455. doi: 10.1086/651706. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alcalá L., Reigadas E., Marín M., Martín A., Catalán P., Bouza E. Impact of clinical awareness and diagnostic tests on the underdiagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases: Official Publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology . 2015;34(8):1515–1525. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2380-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials