Polygenic Score for Smoking is associated with Externalizing Psychopathology and Disinhibited Personality Traits but not Internalizing Psychopathology in Adolescence
- PMID: 35003907
- PMCID: PMC8741064
- DOI: 10.1177/21677026211002117
Polygenic Score for Smoking is associated with Externalizing Psychopathology and Disinhibited Personality Traits but not Internalizing Psychopathology in Adolescence
Abstract
We examined whether a polygenic score (PGS) for smoking measured genetic risk for general behavioral disinhibition by estimating its associations with externalizing and internalizing psychopathology and related personality traits at multiple time points in adolescence (ages 11, 14, and 17 years; N = 3225). The smoking PGS had strong associations with the stable variance across time for all the externalizing measures (mean standardized β = .27), agreeableness (β = -.22, 95% CI: -.28, -.16), and conscientiousness (β = -.19, 95% CI: -.24, -.13), but was not significantly associated with internalizing measures (mean β = .06) or extraversion (β = .01, 95% CI: -.05, .07). After controlling for smoking at age 17, the associations with externalizing, low agreeableness, and low conscientiousness remained statistically significant. The smoking PGS measures genetic influences that contribute to a spectrum of phenotypes related to behavioral disinhibition including externalizing psychopathology and normal-range personality traits related to behavioral control, but not internalizing psychopathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
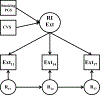
Figures
References
-
- Akingbuwa WA, Hammerschlag AR, Jami ES, et al. , Bipolar Disorder and Major Depressive Disorder Working Groups of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. (2020). Genetic associations between childhood psychopathology and adult depression and associated traits in 42,998 individuals: A meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry, 77, 715–728. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- R01 AA009367/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA034606/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AA026632/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007477/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA024433/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA042755/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA005147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA044283/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013240/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA009367/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA028259/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA037280/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH015755/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA037904/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA046413/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
