Rare Case of a Young Female With Co-existent Hydatidiform Mole and Pulmonary Metastases: An Underrecognized Entity
- PMID: 35004059
- PMCID: PMC8730798
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.20245
Rare Case of a Young Female With Co-existent Hydatidiform Mole and Pulmonary Metastases: An Underrecognized Entity
Abstract
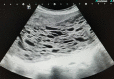
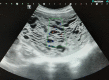
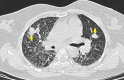
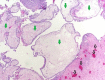
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) comprises placental-site hydatidiform moles, invasive moles, or choriocarcinoma which are of unknown etiology and characterized by abnormal proliferation of gestational trophoblastic tissue. Furthermore, malignant GTD is also characterized by hematogenous spread to distant metastatic sites. Nevertheless, early diagnosis of gestational trophoblastic disease is important to ensure timely and successful management of the clinical condition and for the preservation of fertility. We report the unusual case of a complete hydatidiform mole to pulmonary metastases in a 27-year-old woman with elevated beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) levels. The placental histopathology showed a complete hydatidiform mole with absent fetal parts. Beta-human chorionic gonadotrophin (β-hCG) levels were found elevated at 893 mIU/mL. The case was discussed at the multidisciplinary tumour board and surgical resection with four cycles of combination chemotherapy was recommended, following which β-hCG normalization was achieved. This case report highlights the importance of clinical vigilance even in low-risk patients. Unexpected findings on ultrasound should involve multidisciplinary input from radiologists and surgical oncologists. A high index of suspicion for gestational trophoblastic disease and imaging follow-up for metastases is imperative.
Keywords: beta-human chorionic gonadotrophin levels; combination chemotherapy; gestational trophoblastic disease; hydatidiform mole; pulmonary metastases.
Copyright © 2021, Reddy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Case of Rapid Transformation from Hydatidiform Mole to Invasive Mole: The Importance of β-hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) Serum Levels in Follow-Up Evaluation.Am J Case Rep. 2021 Jun 15;22:e931156. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.931156. Am J Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34127641 Free PMC article.
-
Gestational trophoblastic diseases - clinical guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, follow-up, and counselling.Dan Med J. 2015 Nov;62(11):A5082. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 26522484
-
Bullae-Forming Pulmonary Metastasis from Choriocarcinoma Presenting as Pneumothorax.Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015 Dec;48(6):435-8. doi: 10.5090/kjtcs.2015.48.6.435. Epub 2015 Dec 5. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015. PMID: 26665116 Free PMC article.
-
Surgery including fertility-sparing treatment of GTD.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2021 Jul;74:97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2020.10.005. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2021. PMID: 33127305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gestational Trophoblastic Disorders: An Update in 2015.Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2015 Oct;75(10):1043-1050. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1558054. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2015. PMID: 26556906 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Does methotrexate (MTX) dosing in a 8-day MTX/FA regimen for the treatment of low-risk gestational trophoblastic neoplasia affect outcomes? The MITO-9 study. Mangili G, Cioffi R, Danese S, et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2018;151:449–452. - PubMed
-
- The role of human chorionic gonadotropin as tumor marker: biochemical and clinical aspects. Sisinni L, Landriscina M. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;867:159–176. - PubMed
-
- Persistent trophoblast disease following partial molar pregnancy. Wielsma S, Kerkmeijer L, Bekkers R, Pyman J, Tan J, Quinn M. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2006;46:119–123. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
