Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Complicated by Adenocarcinoma and Organizing Pneumonia
- PMID: 35004080
- PMCID: PMC8727334
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.20916
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Complicated by Adenocarcinoma and Organizing Pneumonia
Abstract
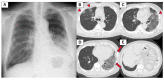
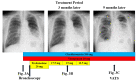
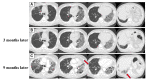
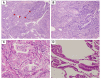
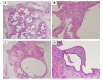
We describe a case of a 77-year-old male with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) complicated by lung adenocarcinoma and organizing pneumonia (OP). On initial examination, physical examination revealed fine crackles in both sides of his chest. There were no physical findings suggestive of collagen disease. Blood tests showed no elevation of C-reactive protein, and lactate dehydrogenase and Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) were within normal limits. A high-resolution CT (HRCT) of the chest showed multiple ground-glass opacities (GGOs) in both lungs, with consolidation and traction bronchiectasis in the left lower lobe. Although a bronchoscopy was performed, no diagnosis could be made. Bronchoalveolar lavage showed elevated lymphocytes, and treatment with prednisolone was started for the possibility of OP. Subsequent chest X-ray and chest CT showed worsening of the shadows over time, and shortness of breath on exertion progressed. Surgical lung biopsy revealed IPF complicated by adenocarcinoma and OP. Although the patient was treated with pemetrexed and carboplatin combination therapy, respiratory failure progressed, and palliative care was decided. There is no report of IPF complicated by adenocarcinoma and OP, and early surgical lung biopsy may be important for diagnosis.
Keywords: adenocarcinoma; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; lung cancer; organizing pneumonia; usual interstitial pneumonia.
Copyright © 2022, Inutsuka et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the Diagnostic Efficacies of Serological Markers KL-6, SP-A, SP-D, CCL2, and CXCL13 in Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia.Respiration. 2019;98(6):534-545. doi: 10.1159/000503689. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Respiration. 2019. PMID: 31665737
-
Evaluation and management of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Respir Investig. 2019 Jul;57(4):300-311. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2019.02.003. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Respir Investig. 2019. PMID: 30853366 Review.
-
Treatment with nintedanib for acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Respirol Case Rep. 2017 Jan 12;5(2):e00215. doi: 10.1002/rcr2.215. eCollection 2017 Mar. Respirol Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28096998 Free PMC article.
-
Practical management of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2015 Jul 22;32(2):90-8. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2015. PMID: 26278687 Review.
-
[Pulmonary surfactant protein gene mutation associated with pediatric interstitial lung disease: a case study and the review of related literature].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Feb;51(2):84-9. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23527967 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1811–1823. - PubMed
-
- Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:0–68. - PubMed
-
- Timing of onset of symptoms in people with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Hewson T, McKeever TM, Gibson JE, Navaratnam V, Hubbard RB, Hutchinson JP. Thorax. 2017 - PubMed
-
- Lung cancer associated with usual interstitial pneumonia. Matsushita H, Tanaka S, Saiki Y, Hara M, Nakata K, Tanimura S, Banba J. Pathol Int. 1995;45:925–932. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
