Nano-Delivery of a Novel Inhibitor of Polynucleotide Kinase/Phosphatase (PNKP) for Targeted Sensitization of Colorectal Cancer to Radiation-Induced DNA Damage
- PMID: 35004293
- PMCID: PMC8733593
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.772920
Nano-Delivery of a Novel Inhibitor of Polynucleotide Kinase/Phosphatase (PNKP) for Targeted Sensitization of Colorectal Cancer to Radiation-Induced DNA Damage
Abstract
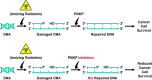
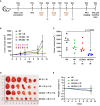
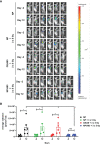
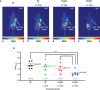
Inhibition of the DNA repair enzyme polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase (PNKP) increases the sensitivity of cancer cells to DNA damage by ionizing radiation (IR). We have developed a novel inhibitor of PNKP, i.e., A83B4C63, as a potential radio-sensitizer for the treatment of solid tumors. Systemic delivery of A83B4C63, however, may sensitize both cancer and normal cells to DNA damaging therapeutics. Preferential delivery of A83B4C63 to solid tumors by nanoparticles (NP) was proposed to reduce potential side effects of this PNKP inhibitor to normal tissue, particularly when combined with DNA damaging therapies. Here, we investigated the radio-sensitizing activity of A83B4C63 encapsulated in NPs (NP/A83) based on methoxy poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(α-benzyl carboxylate-ε-caprolactone) (mPEO-b-PBCL) or solubilized with the aid of Cremophor EL: Ethanol (CE/A83) in human HCT116 colorectal cancer (CRC) models. Levels of γ-H2AX were measured and the biodistribution of CE/A83 and NP/A83 administered intravenously was determined in subcutaneous HCT116 CRC xenografts. The radio-sensitization effect of A83B4C63 was measured following fractionated tumor irradiation using an image-guided Small Animal Radiation Research Platform (SARRP), with 24 h pre-administration of CE/A83 and NP/A83 to Luc+/HCT116 bearing mice. Therapeutic effects were analyzed by monitoring tumor growth and functional imaging using Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and [18F]-fluoro-3'-deoxy-3'-L:-fluorothymidine ([18F]FLT) as a radiotracer for cell proliferation. The results showed an increased persistence of DNA damage in cells treated with a combination of CE/A83 or NP/A83 and IR compared to those only exposed to IR. Significantly higher tumor growth delay in mice treated with a combination of IR and NP/A83 than those treated with IR plus CE/A83 was observed. [18F]FLT PET displayed significant functional changes for tumor proliferation for the drug-loaded NP. This observation was attributed to the higher A83B4C63 levels in the tumors for NP/A83-treated mice compared to those treated with CE/A83. Overall, the results demonstrated a potential for A83B4C63-loaded NP as a novel radio-sensitizer for the treatment of CRC.
Keywords: DNA damage; DNA repair; PNKP; colorectal cancer; combination therapy; ionizing radiation; nanoparticle; radio-sensitization.
Copyright © 2021 Sadat, Wuest, Paiva, Munira, Sarrami, Sanaee, Yang, Paladino, Binkhathlan, Karimi-Busheri, Martin, Jirik, Murray, Gamper, Hall, Weinfeld and Lavasanifar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Material in this manuscript has been included in recent US patent applications. AL is Vice-President of Meros Polymers which has the license to mPEO-b-PBCL polymer used in this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Kennedy RH, Francis EA, Wharton R, Blazeby JM, Quirke P, West NP, et al. Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial of Conventional Versus Laparoscopic Surgery for Colorectal Cancer Within an Enhanced Recovery Programme: Enrol. J Clin Oncol (2014) 32(17):1804–11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.54.3694 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Koopman M, Antonini NF, Douma J, Wals J, Honkoop AH, Erdkamp FL, et al. Sequential Versus Combination Chemotherapy With Capecitabine, Irinotecan, and Oxaliplatin in Advanced Colorectal Cancer (CAIRO): A Phase III Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet (2007) 370(9582):135–42. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61086-1 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

