Prognostic Role of Soluble Programmed Death Ligand 1 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35004295
- PMCID: PMC8732757
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.774131
Prognostic Role of Soluble Programmed Death Ligand 1 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to explore whether soluble programmed death ligand 1 (sPD-L1) is a potential prognostic biomarker in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: A comprehensive search of electronic databases was carried out. Original studies with inclusion of sPD-L1, progression-free survival, and overall survival in NSCLC were eligible. The primary endpoints were overall survival and progression-free survival. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were applied for data analysis.
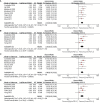
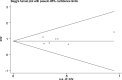
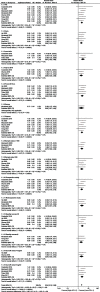
Results: Eight studies involving 710 patients with NSCLC were included in the analysis. A pooled data analysis revealed that high levels of sPD-L1 were correlated with poorer overall survival (HR = 2.34; 95% CI = 1.82-3.00; P < 0.001) and progression-free survival (HR = 2.35; 95% CI = 1.62-3.40, P < 0.001). A subgroup analysis revealed that high levels of sPD-L1 were correlated with poor overall survival in patients treated with immunotherapy (HR = 2.40; 95% CI = 1.79-3.22; P < 0.001).
Conclusion: This pooled analysis of published data suggests that sPD-L1 may serve as a readily available biomarker for survival in NSCLC patients treated with ICI based treatment. Prospective studies with well-designed standard assessment methods should be conducted to validate the prognostic role of sPD-L1 in NSCLC.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42021283177.
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer; overall survival; prognosis; soluble programmed death ligand 1.
Copyright © 2021 Liao, Zhao, Qian, Ling, Chen, Li and Kong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The predictive role of soluble programmed death ligand 1 in digestive system cancers.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 13;13:1170220. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1170220. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37519785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of soluble programmed cell death-1 (sPD-1) and soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022 Jul;71(7):1633-1644. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03103-2. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022. PMID: 34750662 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and predictive significance of soluble programmed death ligand 1 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 31;13(8):1888-1906. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-392. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39263019 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis.Immunotherapy. 2022 Aug;14(12):945-956. doi: 10.2217/imt-2021-0238. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Immunotherapy. 2022. PMID: 35822688 Review.
-
Soluble PD-L1 and Serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-B May Independently Predict Prognosis in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Pembrolizumab.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 27;17(3):421. doi: 10.3390/cancers17030421. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941790 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Soluble immune checkpoint molecules in cancer risk, outcomes prediction, and therapeutic applications.Biomark Res. 2024 Sep 2;12(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00647-0. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39218939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble biomarkers to predict clinical outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer treated by immune checkpoints inhibitors.Front Immunol. 2023 May 22;14:1171649. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1171649. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37283751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble PD-L1 as a Prognostic Factor for Immunotherapy Treatment in Solid Tumors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 21;23(22):14496. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214496. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430974 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-treatment soluble PD-L1 as a predictor of overall survival for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 May;72(5):1061-1073. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03328-9. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36385210 Free PMC article.
-
Progresses in biomarkers for cancer immunotherapy.MedComm (2020). 2023 Oct 3;4(5):e387. doi: 10.1002/mco2.387. eCollection 2023 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37799808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

