Clinical Trials of Oncolytic Viruses in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35004328
- PMCID: PMC8733599
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.803050
Clinical Trials of Oncolytic Viruses in Breast Cancer
Abstract
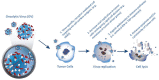
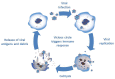
Breast cancer is the second most common kind of cancer worldwide and oncolytic viruses may offer a new treatment approach. There are three different types of oncolytic viruses used in clinical trials; (i) oncolytic viruses with natural anti-neoplastic properties; (ii) oncolytic viruses designed for tumor-selective replication; (iii) oncolytic viruses modified to activate the immune system. Currently, fourteen different oncolytic viruses have been investigated in eighteen published clinical trials. These trials demonstrate that oncolytic viruses are well tolerated and safe for use in patients and display clinical activity. However, these trials mainly studied a small number of patients with different advanced tumors including some with breast cancer. Future trials should focus on breast cancer and investigate optimal routes of administration, occurrence of neutralizing antibodies, viral gene expression, combinations with other antineoplastic therapies, and identify subtypes that are particularly suitable for oncolytic virotherapy.
Keywords: breast cancer; clinical trials; oncolytic virus; review; virotherapy.
Copyright © 2021 Carter, Koch, Lauer and Hartkopf.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oncolytic Virotherapy for Cancer: Clinical Experience.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 13;9(4):419. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040419. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33924556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of oncolytic viruses for cancer therapy.Transl Res. 2021 Nov;237:98-123. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.04.008. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33905949 Review.
-
The Clinical Advances of Oncolytic Viruses in Cancer Immunotherapy.Cureus. 2023 Jun 21;15(6):e40742. doi: 10.7759/cureus.40742. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37485097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Application of Oncolytic Viruses: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 12;21(20):7505. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207505. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33053757 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of a Novel Mesothelin-Targeted Oncolytic Herpes Virus and Implemented Strategies for Manufacturing.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 6;22(2):477. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020477. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33418877 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oncolytic Adenovirus for the Targeting of Paclitaxel-Resistant Breast Cancer Stem Cells.Viruses. 2024 Apr 5;16(4):567. doi: 10.3390/v16040567. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675909 Free PMC article.
-
New hopes for the breast cancer treatment: perspectives on the oncolytic virus therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 21;15:1375433. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1375433. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38576614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic enhancement of oncolytic virus M1 by inhibiting JAK‒STAT pathway.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Jun;14(6):2554-2566. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.03.007. Epub 2024 Mar 10. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38828147 Free PMC article.
-
CAR expression in invasive breast carcinoma and its effect on adenovirus transduction efficiency.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 10;26(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01880-z. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39256827 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic advancements in breast cancer treatment: a review.Discov Oncol. 2025 Feb 7;16(1):127. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01884-x. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39918655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Society AC. Breast Cancer Facts & 017-2018. Atlanta: American Cancer Society, Inc; (2017).
-
- Swain SM, Kim SB, Cortes J, Ro J, Semiglazov V, Campone M, et al. Pertuzumab, Trastuzumab, and Docetaxel for HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer (CLEOPATRA Study): Overall Survival Results From a Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol (2013) 14:461–71. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70130-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

