Red Blood Cell Extracellular Vesicle-Based Drug Delivery: Challenges and Opportunities
- PMID: 35004730
- PMCID: PMC8739511
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.761362
Red Blood Cell Extracellular Vesicle-Based Drug Delivery: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
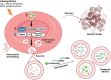
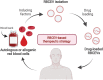
Recently, red blood cell-derived extracellular vesicles (RBCEVs) have attracted attention for clinical applications because of their safety and biocompatibility. RBCEVs can escape macrophages through the binding of CD47 to inhibitory receptor signal regulatory protein α. Furthermore, genetic materials such as siRNA, miRNA, mRNA, or single-stranded RNA can be encapsulated within RBCEVs and then released into target cells for precise treatment. However, their side effects, half-lives, target cell specificity, and limited large-scale production under good manufacturing practice remain challenging. In this review, we summarized the biogenesis and composition of RBCEVs, discussed the advantages and disadvantages of RBCEVs for drug delivery compared with synthetic nanovesicles and non-red blood cell-derived EVs, and provided perspectives for overcoming current limitations to the use of RBCEVs for clinical applications.
Keywords: RBCEVs; cancer; clinical application; exosome; extracellular vesicles; microvesicles; therapeutic drug delivery.
Copyright © 2021 Chiangjong, Netsirisawan, Hongeng and Chutipongtanate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Drug Delivery: A Focus on Red Blood Cells-Derived EVs.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 21;15(2):365. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020365. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoclast-targeted delivery of anti-miRNA oligonucleotides by red blood cell extracellular vesicles.J Control Release. 2023 Jun;358:259-272. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.04.043. Epub 2023 May 5. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37121514
-
Endocytosis of red blood cell extracellular vesicles by macrophages leads to cytoplasmic heme release and prevents foam cell formation in atherosclerosis.J Extracell Vesicles. 2023 Aug;12(8):e12354. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12354. J Extracell Vesicles. 2023. PMID: 37553837 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Red Blood Cells and Their Evolving Roles in Health, Coagulopathy and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 25;22(1):153. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010153. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient and highly reproducible production of red blood cell-derived extracellular vesicle mimetics for the loading and delivery of RNA molecules.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 25;14(1):14610. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65623-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38918594 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles: Emergent and Multiple Sources in Wound Healing Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 28;24(21):15709. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115709. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression analysis revealed downregulation of complement receptor 1 in clonal B cells in cold agglutinin disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 Mar 12;216(1):45-54. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad135. Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38133636 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporation of recombinant proteins into extracellular vesicles by Lactococcus cremoris.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 13;15(1):1768. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86492-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39815011 Free PMC article.
-
Coding Therapeutic Nucleic Acids from Recombinant Proteins to Next-Generation Vaccines: Current Uses, Limitations, and Future Horizons.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug;66(8):1853-1871. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00821-z. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37578574 Review.
-
Addressing Heterogeneity in Direct Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Analogs by Membrane Sensing Peptides as Pan-Vesicular Affinity Probes.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(29):e2400533. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400533. Epub 2024 May 31. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38822532 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

