Effect of Multiple-Nutrient Supplement on Muscle Damage, Liver, and Kidney Function After Exercising Under Heat: Based on a Pilot Study and a Randomised Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35004797
- PMCID: PMC8733564
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.740741
Effect of Multiple-Nutrient Supplement on Muscle Damage, Liver, and Kidney Function After Exercising Under Heat: Based on a Pilot Study and a Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
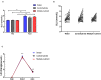
Objective: This study explored the effect of multiple-nutrient supplementation on muscle damage and liver and kidney function after vigorous exercise under heat. Methods: After an initial pilot trial comprising 89 male participants, 85 participants were recruited and assigned into three groups: a multiple-nutrient (M) group, a glucose (G) group, and a water (W) group. Multiple-nutrient supplements contain glucose, fructose, maltose, sodium, potassium, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin C, vitamin K, and taurine. Participants were organised to take a 3-km running test (wet-bulb globe temperature 32°C) after a short-term (7 days) supplement. Blood samples were obtained to detect biochemical parameters [glucose (GLU), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), uric acid (UA), creatinine (Cr), creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and lactic acid], inflammation factors [interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)], and oxidative stress biomarkers [superoxide dismutase (SOD) and 8-iso-prostaglandin F (2alpha) (8-iso-PGF2α)]. Results: In the pilot trial, BUN decreased significantly in the M and G groups immediately after the running test. AST, Cr, and UA were significantly reduced 24 h after the running test with single-shot multiple-nutrient supplementation. In the short-term trial, multiple nutrients further prevented the elevation of CK (p = 0.045) and LDH (p = 0.033) levels 24 h after strenuous exercise. Moreover, we found that multiple nutrients significantly reduced IL-6 (p = 0.001) and TNF-α (p = 0.015) elevation immediately after exercise. Simultaneously, SOD elevation was significantly higher in the M group immediately after exercising than in the other two groups (p = 0.033). 8-iso-PGF2α was reduced in the M group 24 h after exercise (p = 0.036). Conclusions: This study found that multiple-nutrient supplementation promoted the recovery of muscle damage and decreased liver and kidney function caused by strenuous exercise in a hot environment, probably through the inhibition of secondary damage induced by increased inflammatory reactions and oxidative stress. In this respect, the current study has important implications for the strategy of nutritional support to accelerate recovery and potentially prevent heat-related illness. This study was prospectively registered on clinicaltrials.gov on June 21, 2019 (ID: ChiCTR1900023988).
Keywords: hot environment; inflammatory reaction; multiple nutrients; oxidative stress; recovery.
Copyright © 2021 Wei, Zhao, Zhang, Gu, Kumar Sarker, Liu, Li, Wang, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effect of Tribulus terrestris supplementation on inflammation, oxidative stress, and performance of recreational runners: study protocol for a randomized placebo-controlled trial.Trials. 2022 Aug 19;23(1):689. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06630-0. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35986353 Free PMC article.
-
[Protective effects of ulinastatin against multiple organic damage after severe burn injury: experimental and clinic studies].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Nov 2;85(41):2889-94. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16324360 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Infrared Low-Level Laser Therapy (Photobiomodulation Therapy) before Intense Progressive Running Test of High-Level Soccer Players: Effects on Functional, Muscle Damage, Inflammatory, and Oxidative Stress Markers-A Randomized Controlled Trial.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 16;2019:6239058. doi: 10.1155/2019/6239058. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31827687 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exercises in hot and humid environment caused liver injury in a rat model.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 30;9(12):e111741. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111741. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25548911 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of Vitamin C Intake on Muscle Damage in Male Adolescents Performing Strenuous Physical Activity.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018 Sep 11;6(9):1594-1598. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.337. eCollection 2018 Sep 25. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30337971 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pterostilbene attenuates intestinal epithelial barrier loss induced by high loading intensity of exercise.Front Nutr. 2022 Aug 4;9:965180. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.965180. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35990348 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 can reverse fatigue behavior in CFS rats by regulating EGFR and affecting Taurine and Mannose 6-phosphate metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 10;14:1163638. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1163638. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37101547 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney fibrosis molecular mechanisms Spp1 influences fibroblast activity through transforming growth factor beta smad signaling.iScience. 2024 May 9;27(9):109839. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109839. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39323737 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

