Integrated Pharmacogenetics Analysis of the Three Fangjis Decoctions for Treating Arrhythmias Based on Molecular Network Patterns
- PMID: 35004871
- PMCID: PMC8739471
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.726694
Integrated Pharmacogenetics Analysis of the Three Fangjis Decoctions for Treating Arrhythmias Based on Molecular Network Patterns
Abstract
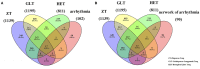
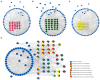
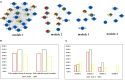
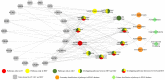
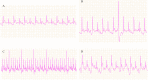
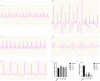
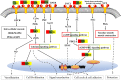
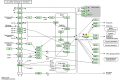
Aim: To explore the diverse target distribution and variable mechanisms of different fangjis prescriptions when treating arrhythmias based on the systems pharmacology. Methods: The active ingredients and their corresponding targets were acquired from the three fangjis [Zhigancao Tang (ZT), Guizhigancao Longgumuli Tang (GLT), and Huanglian E'jiao Tang (HET)] and the arrhythmia-related genes were identified based on comprehensive database screening. Networks were constructed between the fangjis and arrhythmia and used to define arrhythmia modules. Common and differential gene targets were identified within the arrhythmia network modules and the cover rate (CR) matrix was applied to compare the contributions of the fangjis to the network and modules. Comparative pharmacogenetics analyses were then conducted to define the arrhythmia-related signaling pathways regulated by the fangjis prescriptions. Finally, the divergence and convergence points of the arrhythmia pathways were deciphered based on databases and the published literature. Results: A total of 187, 105, and 68 active ingredients and 1,139, 1,195, and 811 corresponding gene targets of the three fangjis were obtained and 102 arrhythmia-related genes were acquired. An arrhythmia network was constructed and subdivided into 4 modules. For the target distribution analysis, 65.4% of genes were regulated by the three fangjis within the arrhythmia network. ZT and GLT were more similar to each other, mainly regulated by module two, whereas HET was divided among all the modules. From the perspective of signal transduction, calcium-related pathways [calcium, cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cGMP)-PKG, and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP)] and endocrine system-related pathways (oxytocin signaling pathway and renin secretion pathways) were associated with all the three fangjis prescriptions. Nevertheless, heterogeneity existed between the biological processes and pathway distribution among the three prescriptions. GLT and HET were particularly inclined toward the conditions involving abnormal hormone secretion, whereas ZT tended toward renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) disorders. However, calcium signaling-related pathways prominently feature in the pharmacological activities of the decoctions. Experimental validation indicated that ZT, GLT, and HET significantly shortened the duration of ventricular arrhythmia (VA) and downregulated the expression of CALM2 and interleukin-6 (IL-6) messenger RNAs (mRNAs); GLT and HET downregulated the expression of CALM1 and NOS3 mRNAs; HET downregulated the expression of CRP mRNA. Conclusion: Comparing the various distributions of the three fangjis, pathways provide evidence with respect to precise applications toward individualized arrhythmia treatments.
Keywords: arrhythmias; fangjis; network pharmacology; precision medicine; target distribution.
Copyright © 2021 Wei, Long, Tan, Xing, Li, Yang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict ofinterest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

