Longevity Factor FOXO3: A Key Regulator in Aging-Related Vascular Diseases
- PMID: 35004893
- PMCID: PMC8733402
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.778674
Longevity Factor FOXO3: A Key Regulator in Aging-Related Vascular Diseases
Abstract
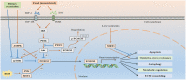
Forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) has been proposed as a homeostasis regulator, capable of integrating multiple upstream signaling pathways that are sensitive to environmental changes and counteracting their adverse effects due to external changes, such as oxidative stress, metabolic stress and growth factor deprivation. FOXO3 polymorphisms are associated with extreme human longevity. Intriguingly, longevity-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in human FOXO3 correlate with lower-than-average morbidity from cardiovascular diseases in long-lived people. Emerging evidence indicates that FOXO3 plays a critical role in vascular aging. FOXO3 inactivation is implicated in several aging-related vascular diseases. In experimental studies, FOXO3-engineered human ESC-derived vascular cells improve vascular homeostasis and delay vascular aging. The purpose of this review is to explore how FOXO3 regulates vascular aging and its crucial role in aging-related vascular diseases.
Keywords: FOXO3; aging; cardiovascular disease; vascular aging; vascular homeostasis.
Copyright © 2021 Zhao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FoxO3 Regulates the Progress and Development of Aging and Aging-Related Diseases.Curr Mol Med. 2023;23(10):991-1006. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666221014140817. Curr Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36239722
-
FOXO3 and related transcription factors in development, aging, and exceptional longevity.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015 Apr;70(4):421-5. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glu044. Epub 2014 Apr 18. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 24747665 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO3 on the Road to Longevity: Lessons From SNPs and Chromatin Hubs.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 Jun 13;17:737-745. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.06.011. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31303978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Association Analysis of Common Variants in FOXO3 Related to Longevity in a Chinese Population.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0167918. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167918. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27936216 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO3: A Major Gene for Human Longevity--A Mini-Review.Gerontology. 2015;61(6):515-25. doi: 10.1159/000375235. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Gerontology. 2015. PMID: 25832544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Large-scale brainstem neuroimaging and genetic analyses provide new insights into the neuronal mechanisms of hypertension.HGG Adv. 2025 Jan 9;6(1):100392. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2024.100392. Epub 2024 Dec 10. HGG Adv. 2025. PMID: 39663699 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 30-mediated deubiquitination of forkhead box O3 promotes the progression of subarachnoid hemorrhage by regulating cGAS/STING pathway.Neuroreport. 2025 Sep 3;36(13):719-727. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000002192. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Neuroreport. 2025. PMID: 40736326 Free PMC article.
-
FOXO3 Longevity Genotype Mitigates Risk Posed by Hypertension on Incident Coronary Artery Disease in Middle-Aged Men: Kuakini Honolulu Heart Program.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024 Dec 1;79(12):glae254. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glae254. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39497655 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of endothelial cell senescence via the miR-217/FOXO3 axis.Biogerontology. 2025 Jul 21;26(4):147. doi: 10.1007/s10522-025-10290-3. Biogerontology. 2025. PMID: 40689999 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective cohort study to develop multi-biomarkers panel to define biological ageing in six different cohorts from newborn to oldest adult: a study protocol.Biol Methods Protoc. 2025 Jul 3;10(1):bpaf053. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpaf053. eCollection 2025. Biol Methods Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40799309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. . Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. (2012) 380:2095–128. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

