Incidence of acute aortic dissections in patients with out of hospital cardiac arrest: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- PMID: 35005212
- PMCID: PMC8717414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2021.100934
Incidence of acute aortic dissections in patients with out of hospital cardiac arrest: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Abstract
Objectives: Acute Aortic dissection (AAD) may present as out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). However, the incidence of this presentation is not well known. Our aim was to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of all observational studies reporting on the incidence of AAD in patients with OHCA.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, CENTRAL, PsycInfo, Web of Science Core Collection and OpenGrey databases from inception to March-2021, for observational studies reporting on the incidence of AAD in patients with OHCA. Data was pooled using a random-effects model of proportions. The primary outcome was the incidence of AAD in OHCA patients. Secondary outcomes were the incidence of type A aortic dissections (TAAD) and type B aortic dissections (TBAD) in OHCA patients, overall mortality following AAD-OHCA and risk of death in AAD-OHCA patients compared to risk of death of non-AAD-OHCA patients.
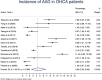
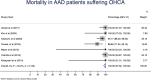
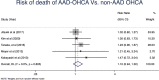
Results: Fourteen studies were included. The pooled calculated incidence of OHCA due to AAD was 4.39% (95 %CI: 2.55; 6.8). Incidence of OHCA due to TAAD was 7.18% (95 %CI: 5.61; 8.93) and incidence of OHCA due to TBAD was 0.47% (95 %CI: 0.18; 0.85). Overall mortality following OHCA due to AAD was 100% (95 %CI: 97.62; 100). The risk of death in AAD-OHCA patients compared with non-AAD-OHCA patients was 1.10 (95 %CI: 0.94; 1.30).
Conclusion: AAD as a cause of OHCA is more frequent than previously thought. Prognosis is dire, as it is invariably lethal. These findings should lead to a higher awareness of AAD when approaching a patient with OHCA and to future studies on this matter.
Keywords: Aortic dissection; Incidence; Meta-analysis; Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest; Systematic review.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Meron G., Kürkciyan I., Sterz F., Tobler K., Losert H., Sedivy R., Laggner A.N., Domanovits H. Non-traumatic aortic dissection or rupture as cause of cardiac arrest: presentation and outcome. Resuscitation. 2004;60(2):143–150. - PubMed
-
- Pleskot M., Babu A., Kajzr J., Kvasnicka J., Stritecky J., Cermakova E., Mestan M., Parizek P., Tauchman M., Tusl Z., Perna P. Characteristics and short-term survival of individuals with out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in the East Bohemian region. Resuscitation. 2006;68(2):209–220. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi S., Yamaguchi Y., Soejima K., Yoshino H. Incidence and characteristics of acute aortic dissection in patients with out-of-hospital cardiopulmonary arrest evaluated by non- contrast computed tomography. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care. 2020;9:S48–S57. - PubMed
-
- Nienaber C.A., Clough R.E. Management of acute aortic dissection. Lancet. 2015;385(9970):800–811. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

