3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethanol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiac injury in a murine model
- PMID: 35005242
- PMCID: PMC8691377
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2021-0125
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethanol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiac injury in a murine model
Abstract
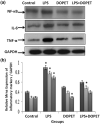
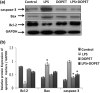
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethanol (DOPET) is a polyphenol found in olive oil. The present study evaluated the protective role of DOPET on LPS provoked septic cardiac injury in a murine model. Four groups were used in the study (n = 3): control, LPS, DOPET alone, and DOPET + LPS. LPS (15 mg/kg; i.p.); they were used to induce cardiac sepsis. The cardiac markers like LDH, CK-MB, and troponin-T, as well as inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6 were measured in the serum. The antioxidants and oxidative stress parameters were measured in cardiac tissues. RT-PCR and western blot methods were done to evaluate the expression of inflammatory mediators and apoptotic markers. DOPET significantly decreased the cardiac markers (LDH, CK-MB, and troponin-T) and TNF-α and IL-6 level in the serum. DOPET effectively reduced the levels of MDA and NO in LPS intoxicated rats. DOPET also increased the levels of antioxidants like SOD, CAT, GPx, and GSH in LPS intoxicated rats. The mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and NF-κB were significantly downregulated by DOPET in cardiac tissues of LPS rats. The protein expression of Bcl-2 was upregulated, and Bax and caspase-3 were downregulated by DOPET. DOPET effectively attenuates LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic mechanisms.
Keywords: DOPET; LPS; apoptosis; cardiac damage; inflammation; sepsis.
© 2021 Lu Zhang et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Balk RA. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS): where did it come from and is it still relevant today? Virulence. 2014;5(1):20–6. - PMC - PubMed
- Balk RA. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS): where did it come from and is it still relevant today? Virulence. 2014;5(1):20–6. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons ML, Chaitman BR, White HD, et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(16):1581–98. - PubMed
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons ML, Chaitman BR, White HD. et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(16):1581–98. - PubMed
-
- Baelani I, Jochberger S, Laimer T, Otieno D, Kabutu J, Wilson I, et al. Availability of critical care resources to treat patients with severe sepsis or septic shock in Africa: a self-reported, continent-wide survey of anaesthesia providers. Crit care. 2011;15(1):R10. - PMC - PubMed
- Baelani I, Jochberger S, Laimer T, Otieno D, Kabutu J, Wilson I. et al. Availability of critical care resources to treat patients with severe sepsis or septic shock in Africa: a self-reported, continent-wide survey of anaesthesia providers. Crit care. 2011;15(1):R10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dkhil MA, Kassab RB, Al-Quraishy S, Abdel-Daim MM, Zrieq R, Abdel Moneim AE. Ziziphus spina-christi (L.) leaf extract alleviates myocardial and renal dysfunction associated with sepsis in mice. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacotherap. 2018;102:64–75. - PubMed
- Dkhil MA, Kassab RB, Al-Quraishy S, Abdel-Daim MM, Zrieq R, Abdel Moneim AE. Ziziphus spina-christi (L.) leaf extract alleviates myocardial and renal dysfunction associated with sepsis in mice. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacotherap. 2018;102:64–75. - PubMed
-
- Zarychanski R, Doucette S, Fergusson D, Roberts D, Houston DS, Sharma S, et al. Early intravenous unfractionated heparin and mortality in septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2008;36(11):2973–9. - PubMed
- Zarychanski R, Doucette S, Fergusson D, Roberts D, Houston DS, Sharma S. et al. Early intravenous unfractionated heparin and mortality in septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2008;36(11):2973–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
