Finerenone in Predominantly Advanced CKD and Type 2 Diabetes With or Without Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Therapy
- PMID: 35005312
- PMCID: PMC8720648
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.10.008
Finerenone in Predominantly Advanced CKD and Type 2 Diabetes With or Without Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Therapy
Abstract
Introduction: FIDELIO-DKD (FInerenone in reducing kiDnEy faiLure and dIsease prOgression in Diabetic Kidney Disease) investigated the nonsteroidal, selective mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist finerenone in patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes (T2D). This analysis explores the impact of use of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor (SGLT-2i) on the treatment effect of finerenone.
Methods: Patients (N = 5674) with T2D, urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of 30 to 5000 mg/g and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25 to <75 ml/min per 1.73 m2 receiving optimized renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade were randomized to finerenone or placebo. Endpoints were change in UACR and a composite kidney outcome (time to kidney failure, sustained decrease in eGFR ≥40% from baseline, or renal death) and key secondary cardiovascular outcomes (time to cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure) (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02540993).
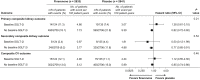
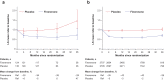
Results: Of 5674 patients, 259 (4.6%) received an SGLT-2i at baseline. Reduction in UACR with finerenone was found with or without use of SGLT-2i at baseline, with ratio of least-squares means of 0.69 (95% CI = 0.66-0.71) and 0.75 (95% CI -= 0.62-0.90), respectively (P interaction = 0.31). Finerenone also significantly reduced the kidney and key secondary cardiovascular outcomes versus placebo; there was no clear difference in the results by SGLT-2i use at baseline (P interaction = 0.21 and 0.46, respectively) or at any time during the trial. Safety was balanced with or without SGLT-2i use at baseline, with fewer hyperkalemia events with finerenone in the SGLT-2i group (8.1% vs. 18.7% without).
Conclusion: UACR improvement was observed with finerenone in patients with CKD and T2D already receiving SGLT-2is at baseline, and benefits on kidney and cardiovascular outcomes appear consistent irrespective of use of SGLT-2i.
Keywords: albuminuria; chronic kidney disease; finerenone; sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors; type 2 diabetes.
© 2021 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of canagliflozin versus finerenone on cardiorenal outcomes: exploratory post hoc analyses from FIDELIO-DKD compared to reported CREDENCE results.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022 Jun 23;37(7):1261-1269. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfab336. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022. PMID: 34850173 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Finerenone and Heart Failure Outcomes by Kidney Function/Albuminuria in Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes.JACC Heart Fail. 2022 Nov;10(11):860-870. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2022.07.013. Epub 2022 Oct 12. JACC Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 36328655 Clinical Trial.
-
Finerenone in Hispanic Patients With CKD and Type 2 Diabetes: A Post Hoc FIDELITY Analysis.Kidney Med. 2023 Aug 1;5(10):100704. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2023.100704. eCollection 2023 Oct. Kidney Med. 2023. PMID: 37745646 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2022 Oct 15;6(6):536-551. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2022.09.002. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes. 2022. PMID: 36277502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-steroidal mineralocorticoid antagonists and hyperkalemia monitoring in chronic kidney disease patients associated with type II diabetes: a narrative review.Postgrad Med. 2024 Mar;136(2):111-119. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2024.2316572. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Postgrad Med. 2024. PMID: 38344772 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-Life Experience on the Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors vs. Finerenone vs. Combination on Albuminuria in Chronic Kidney Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 26;14(13):1357. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131357. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001247 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Disease in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Putative Contributions of Mineralocorticoid Receptors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 23;24(3):2245. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032245. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Finerenone in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes According to Baseline HbA1c and Insulin Use: An Analysis From the FIDELIO-DKD Study.Diabetes Care. 2022 Apr 1;45(4):888-897. doi: 10.2337/dc21-1944. Diabetes Care. 2022. PMID: 35061867 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Water and electrolyte abnormalities in novel pharmacological agents for kidney disease and cancer.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025 May;29(5):521-533. doi: 10.1007/s10157-025-02635-6. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39937358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Potassium Binders in Reduction of Hyperkalemia and Optimization of RAAS Inhibitors Treatment in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease or Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Drugs. 2025 Aug;85(8):1013-1031. doi: 10.1007/s40265-025-02198-6. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40542996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Incidence, prevalence, patient characteristics, and treatment modalities United States Renal Data System. Published 2020. Accessed 13 April 2021. https://adr.usrds.org/2020/end-stage-renal-disease/1-incidence-prevalenc...
-
- Buse J.B., Wexler D.J., Tsapas A., et al. 2019 update to: management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018 A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) [published correction appears in Diabetologia. 2020;63:1667] Diabetologia. 2020;63:221–228. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05039-w. - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

