Perineural steroid injections around ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric, and genitofemoral nerves for treatment of chronic refractory neuropathic pain: A retrospective study
- PMID: 35005356
- PMCID: PMC8730627
- DOI: 10.1080/24740527.2017.1403846
Perineural steroid injections around ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric, and genitofemoral nerves for treatment of chronic refractory neuropathic pain: A retrospective study
Abstract
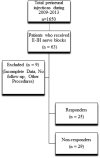
Background: Perineural local anaesthetic and steroid injections around ilioinguinal (II), iliohypogastric (IH), and genitofemoral (GF) nerves are often performed to treat chronic refractory neuropathic pain in the lower abdomen and groin, but there is a lack of published data on outcomes of these interventions. Aims: The objective of this retrospective study was to evaluate analgesic outcomes of ultrasound-guided II, IH, and GF nerve blocks in patients with chronic neuropathic pain in the lower abdominal wall and groin. Methods: Analgesic outcomes were assessed at 6 weeks after injections and patients were classified as "responders" if the numerical rating scale for pain score reduced by 30% or more. Variables analyzed for impact on outcomes included demographics, intensity of pain and duration, etiology, dose of opioid, presence of anxiety, depression, and diabetes mellitus. Results: In this cohort of 54 patients with severe baseline pain who had failed to receive analgesic benefit from recommended first- and second-line medications for neuropathic pain, 30 patients had history of surgery and 24 had pain secondary to visceral inflammatory pathologies. Twenty-five (46.3%) patients were identified as responders. A majority of the patients in this cohort had pain for more than one year. There was a higher incidence of diabetes mellitus in nonresponders compared to responders but the difference was not significant (14% and 0%, respectively; P = 0.115). Conclusions: Ultrasound-guided perineural steroids can ameliorate chronic refractory abdominal wall and groin neuropathic pain in patients who have failed to respond to conventional medical management at 6 weeks after the procedures.
Contexte: L’anesthésie locorégionale périneurale et les injections de stéroïdes à proximité du nerf ilio-inguinal (II), du nerf ilio-hypogastrique (IH) et du nerf génito-fémoral (GF) sont souvent utilisées pour traiter la douleur neuropathique chronique réfractaire dans le bas-ventre et dans l’aine, mais peu de données ont été publiées sur les résultats de ces interventions.But: L’objectif de cette étude rétrospective était d’évaluer les résultats analgésiques du blocage des nerfs II, IH et GF guidé par ultrasons chez des patients souffrant de douleur neuropathique chronique dans la paroi du bas-ventre et dans l’aine.Méthodes: Les résultats analgésiques ont été évalués six semaines après les injections et les patients ont été classés « répondeurs » si le score obtenu sur l’échelle numérique pour la douleur avait diminué de 30 % ou plus. Les variables analysées pour leur effet sur les résultats comprenaient les données démographiques; l’intensité et la durée de la douleur; l’étiologie; le dose d’opiacés, la présence d’anxiété; la dépression; et le diabète sucré.Résultats: Parmi cette cohorte de 54 patients souffrant d’une douleur sévère au départ pour lesquels les médications de première et de deuxième ligne recommandées pour la douleur neuropathique n’avaient pas été bénéfiques, 30 patients avaient une histoire de chirurgie et 24 avaient des douleurs secondaires à des pathologies inflammatoires viscérales. 25 patients (46,3 %) ont été identifiés comme répondants. La majorité des patients de cette cohorte ressentaient de la douleur depuis plus d’un an. Il y avait une plus grande incidence de diabète sucré chez les non-répondeurs comparativement aux répondeurs mais la différence n’était pas significative (14 % et 0 % respectivement; p = 0,115).Conclusions: Les stéroïdes périneuraux guidés par ultrasons peuvent améliorer la douleur neuropathique chronique réfractaire dans la paroi abdominale et dans l’aine chez les patients qui n’ont pas répondu à la prise en charge médicale conventionnelle six semaines après les procédures.
Keywords: abdominal wall; iliohypogastric nerve; ilioinguinal nerve; injection; nerve block; neuropathic pain; steroids.
© 2017 Rajinikanth Sundara Rajan, Anuj Bhatia, Philip W. H. Peng and Allan S. Gordon. Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No external funding was used for this study. The authors do not have any conflict of interests relevant to this study.
Figures
References
-
- Wallander MA, Johansson S, Ruigomez A, Garcia Rodriguez LA.. Unspecified abdominal pain in primary care: the role of gastrointestinal morbidity. Int J Clin Pract. 2007;61:1663–1670. - PubMed
-
- Srinivasan R, Greenbaum DS. Chronic abdominal wall pain: a frequently overlooked problem. Practical approach to diagnosis and management. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:824–830. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources