Validation of the Adolescent Pediatric Pain Tool for the Multidimensional Measurement of Pain in Children and Adolescents Diagnosed with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- PMID: 35005403
- PMCID: PMC8730568
- DOI: 10.1080/24740527.2019.1626705
Validation of the Adolescent Pediatric Pain Tool for the Multidimensional Measurement of Pain in Children and Adolescents Diagnosed with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Abstract
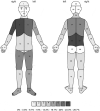
Background: The Adolescent Pediatric Pain Tool (APPT) is a self-reported, multidimensional assessment of pain location, intensity, and quality in children and adolescents. Yet, it has not been validated for use in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). Aims: This study aimed to validate and evaluate the feasibility of the APPT for pain assessment in children and adolescents with OI. Methods: A prospective observational study was conducted at a university-affiliated pediatric hospital in Canada. Thirty-three children and adolescents with OI participated by completing the APPT pre-bisphosphonate intravenous infusion and 1 week post-bisphosphonate intravenous infusion. Main outcomes were internal consistency, convergent and discriminative validity, and feasibility. Results: The Kuder-Richardson test of internal consistency was 0.863, 0.661, and 0.729 for the Sensory, Affective, and Evaluative subscales, respectively. For the entire pain quality scale, the Cronbach's alpha was 0.835. Regarding convergent validity, a moderate correlation was observed between the ratings on the pain intensity scale and the Faces Pain Scale-Revised (Spearman's rho = 0.711). Patients for whom pain was a problem reported higher pain intensity (Mann Whitney U = 41.50, P = 0.032) and more pain quality descriptors (Mann Whitney U = 45.50, P = 0.020) and painful body areas (Mann-Whitney U = 25.50, P = 0.001) than those for whom it was not (Mann-Whitney U, P < 0.05). In terms of feasibility, completing the tool may require a considerable time commitment and assistance from a clinician or parent, especially if the patient is experiencing pain and provides detailed pain location and quality information by completing the APPT. Conclusions: This study suggests that the APPT is valid for the multidimensional assessment of pain in children and adolescents with OI, but feasibility needs to be enhanced.
Contexte: L’outil d’évaluation de la douleur des adolescents en pédiatrie (APPT) est une évaluation multidimensionnelle auto-déclarée de l’emplacement, de l’intensité et de la qualité de la douleur chez les enfants et les adolescents. Toutefois, l’utilisation de cet outil auprès des enfants et des adolescents souffrant d’ostéogénèse imparfaite n’a pas encore été validée.But: Cette étude avait pour but de valider et d’évaluer la faisabilité de l’APPT pour l’évaluation de la douleur dans cette population.Méthodes: Une étude observationnelle prospective a été menée dans un centre hospitalier universitaire à vocation pédiatrique au Canada. Trente-trois enfants et adolescents atteints d’ostéogénèse imparfaite ont participé à cette étude en répondant à l’APPT avant l’infusion intraveineuse de bisphosphonate et une semaine après celle-ci. Les principaux résultats étaient la cohérence interne, la validation convergente et discriminante, et la faisabilité.Résultats: Le résultat du test de Kuder-Richardson pour mesurer la cohérence interne était de 0,863 pour le sensoriel, 0,661 pour l’affectif et 0,729 pour les sous-échelles d’évaluation. Pour l’échelle de qualité de la douleur au complet, l’indice alpha de Cronbach était de 0,835. En ce qui concerne la validation convergente, une corrélation modérée a été observée entre les scores obtenus à l’échelle d’intensité de la douleur et le FPS-R (Rho de Spearman= 0,711). Les patients pour lesquels la douleur était problématique ont fait état d’une intensité de la douleur plus élevée, ont eu recours à un plus grand nombre de descripteurs de la qualité de la douleur et ont identifié davantage de parties du corps douloureuses que ceux pour lesquels la douleur n’était pas problématique (Mann-Whitney U, p < 0,05). En ce qui concerne la faisabilité, le temps requis pour répondre au questionnaire peut être considérable et l’aide d’un clinicien ou d’un parent peut être nécessaire, particulièrement si le patient ressent de la douleur et donne de l’information détaillée sur la localisation et la qualité de la douleur en répondant à l’APPT.Conclusions: Selon cette étude, l’APPT est valide pour l’évaluation multidimensionnelle de la douleur chez les enfants et les adolescens souffrant d’oastéogénèse imparfaite, mais sa faisabilité doit être améliorée.
Keywords: Psychometrics; orthopedic; pain assessment; pediatric pain.
© 2019 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pain and quality of life of children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta over a bisphosphonate treatment cycle.Eur J Pediatr. 2018 Jun;177(6):891-902. doi: 10.1007/s00431-018-3127-9. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Eur J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29637375
-
Adolescent pediatric pain tool for multidimensional measurement of pain in children and adolescents.Pain Manag Nurs. 2014 Sep;15(3):694-706. doi: 10.1016/j.pmn.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Pain Manag Nurs. 2014. PMID: 23870767 Free PMC article.
-
Translation, Cross-Cultural Adaptation, and Validation of the Adolescent Pediatric Pain Tool (APPT) for Multidimensional Measurement of Pain in Children and Adolescents.Pain Manag Nurs. 2019 Dec;20(6):549-555. doi: 10.1016/j.pmn.2019.06.004. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Pain Manag Nurs. 2019. PMID: 31447300
-
Multidimensional assessment using the adolescent pediatric pain tool: a case report.J Spec Pediatr Nurs. 2005 Jul-Sep;10(3):115-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6155.2005.00023.x. J Spec Pediatr Nurs. 2005. PMID: 16083431 Review.
-
Pain Experiences of Children and Adolescents With Osteogenesis Imperfecta: An Integrative Review.Clin J Pain. 2017 Mar;33(3):271-280. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000395. Clin J Pain. 2017. PMID: 27258996 Review.
Cited by
-
A multicenter study to evaluate pain characteristics in osteogenesis imperfecta.Am J Med Genet A. 2023 Jan;191(1):160-172. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.63009. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Am J Med Genet A. 2023. PMID: 36271817 Free PMC article.
-
The Design, Development, and Usability Testing of an eHealth Program for Youths With Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Protocol for a 2-Phase User-Centered Mixed Methods Study.JMIR Res Protoc. 2023 Jun 23;12:e47524. doi: 10.2196/47524. JMIR Res Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37351933 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources