Characterizing the host response to rhPDGF-BB in a rat spinal arthrodesis model
- PMID: 35005440
- PMCID: PMC8717117
- DOI: 10.1002/jsp2.1173
Characterizing the host response to rhPDGF-BB in a rat spinal arthrodesis model
Abstract
Background: Due to the constraints surrounding autograft bone, surgeons have turned to osteoinductive agents to augment spinal fusion. Reports of complications and questionable efficacy slowed the adoption of these alternatives. Recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor B homodimer (rhPDGF-BB) has been Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved (Augment) to promote fusion in other areas of orthopedics, but its characterization in spine fusion has not yet been tested. The purpose of this study is to characterize the host response to PDGF-BB in vivo.
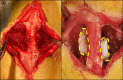
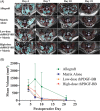
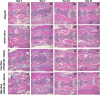
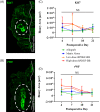
Methods: Eighty female Fischer rats underwent L4-5 posterolateral fusion using one of four implant types: (a) iliac crest syngeneic allograft harvested from syngeneic donors, (b) β-TCP/bovine collagen matrix (β-TCP/Col) with sodium acetate buffer, (c) β-TCP/Col with 0.3 mg/mL "low dose," or (d) β-TCP/Col with 3.0 mg/mL "high dose" of rhPDGF-BB. Animals underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and serum cytokine quantification at 4, 7, 10, and 21 days, postoperatively. Tissues were processed for immunofluorescence staining for Ki67 and von Willebrand factor (vWF) to assess neovascularization.
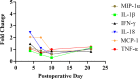
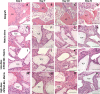
Results: MRI demonstrated no differences in fluid accumulation among the four treatment groups at any of the time points. Serum cytokine analysis showed no clinically significant differences between treatment groups in 20 of the 27 cytokines. Inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-18, MCP-1, MIP-1α, TNF-α were not induced by rhPDGF-BB. Histology showed no differences in cell infiltration, and Ki67 and vWF immunofluorescence staining was similar among groups.
Conclusions: rhPDGF-BB delivered with a β-TCP/Col matrix exerts no exaggerated systemic or local host inflammatory response when compared to iliac crest syngeneic allograft bone or the control carrier. rhPDGF-BB mixed with a β-TCP/Col matrix could be a viable and safe biologic alternative to syngeneic allograft in spine fusion. Further studies need to be performed to evaluate efficacy in this setting.
Keywords: MRI; PDGF; arthrodesis; biologic; cytokine; platelet‐derived growth factor; spine surgery.
© 2021 The Authors. JOR Spine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Orthopaedic Research Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Wellington K. Hsu is an active consultant for Wright Medical.
Figures
References
-
- Rajaee SS, Bae HW, Kanim LEA, Delamarter RB. Spinal fusion in the United States: analysis of trends from 1998 to 2008. Spine. 2012;37(1):67‐76. - PubMed
-
- Fowler BL, Dall BE, Rowe DE. Complications associated with harvesting autogenous iliac bone graft. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1995;24(12):895‐903. - PubMed
-
- Goulet JA, Senunas LE, DeSilva GL, Greenfield ML. Autogenous iliac crest bone graft. Complications and functional assessment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;339:76‐81. - PubMed
-
- Muchow RD, Hsu WK, Anderson PA. Histopathologic inflammatory response induced by recombinant bone morphogenetic protein‐2 causing radiculopathy after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 2010;10(9):e1‐e6. - PubMed
-
- Pradhan BB, Bae HW, Dawson EG, Patel VV, Delamarter RB. Graft resorption with the use of bone morphogenetic protein: lessons from anterior lumbar interbody fusion using femoral ring allografts and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein‐2. Spine. 2006;31(10):E277‐E284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

