Magnitude of Diurnal Change in Retinal Vessel Density: Comparison Between Exfoliative Glaucoma and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
- PMID: 35005505
- PMCID: PMC8651017
- DOI: 10.14744/bej.2021.66934
Magnitude of Diurnal Change in Retinal Vessel Density: Comparison Between Exfoliative Glaucoma and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate the magnitude of diurnal fluctuation in the superficial parafoveal vessel density (pfVD) and radial peripapillary capillary-peripapillary vessel density (RPC-ppVD) in exfoliative glaucoma (XFG) patients using optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) and to compare the findings with those of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) patients with glaucomatous damage of comparable severity.
Methods: A total of 50 patients with XFG and 48 with POAG were examined in this retrospective cross-sectional study. The OCTA readings and intraocular pressure (IOP) values were obtained at 9 am, 11 am, 2 pm, and 4 pm on the same day. The maximal change in the IOP and vessel density (VD) values was evaluated to determine the magnitude of diurnal variation.
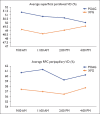
Results: No significant difference was found in the magnitude of the average diurnal superficial-pfVD, RPC-ppVD and IOP change between the XFG and POAG groups. Comparison of the diurnal variation of sub-sector VD revealed that the magnitude of the diurnal variation in the VD of the inferonasal peripapillary and superior parafoveal regions was greater in the XFG group than that of the POAG group (p=0.004 and p=0.021, respectively). Furthermore, the differences persisted after correcting for the confounding factors of IOP, mean deviation (MD), and global retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) values. The magnitude of the average superficial-pfVD and the average RPC-ppVD was not correlated with the MD, total ganglion cell complex, global RNFL, or the magnitude of IOP values in either group.
Conclusion: The eyes of XFG patients demonstrated more significant diurnal fluctuation in VD (including the superior superficial-pfVD as well as the inferonasal RPC-ppVD) when compared with POAG patients, despite no statistical significance between groups in the IOP variation.
Keywords: Ganglion cell complex; magnitude of diurnal variation; optical coherence tomography angiography; parafoveal vessel density; peripapillary vessel density; retinal nerve fiber layer.
Copyright: © 2021 by Beyoglu Eye Training and Research Hospital.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Diurnal Fluctuation in Parafoveal and Peripapillary Vascular Density Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Patients with Exfoliative Glaucoma and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma.Curr Eye Res. 2021 Jan;46(1):96-106. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1784437. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Curr Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 32546011
-
Quantitative Analysis of Microvasculature in Macular and Peripapillary Regions in Early Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma.Curr Eye Res. 2020 May;45(5):629-635. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2019.1676912. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Curr Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31587582
-
Peripapillary and Macular Vessel Density Measurement by Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Pseudoexfoliation and Primary Open-angle Glaucoma.J Glaucoma. 2020 May;29(5):381-385. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000001464. J Glaucoma. 2020. PMID: 32079991
-
[A challenge to primary open-angle glaucoma including normal-pressure. Clinical problems and their scientific solution].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012 Mar;116(3):233-67; discussion 268. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 22568103 Review. Japanese.
-
The impact of intraocular pressure on optical coherence tomography angiography: A review of current evidence.Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jan 3;38(2):144-151. doi: 10.4103/sjopt.sjopt_112_23. eCollection 2024 Apr-Jun. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38988792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bochicchio S, Milani P, Urbini LE, Bulone E, Carmassi L, Fratantonio E, et al. Diurnal stability of peripapillary vessel density and nerve fiber layer thickness on optical coherence tomography angiography in healthy, ocular hypertension and glaucoma eyes. Clin Ophthalmol. 2019;13:1823–32. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Müller VC, Storp JJ, Kerschke L, Nelis P, Eter N, Alnawaiseh M. Diurnal variations in flow density measured using optical coherence tomography angiography and the impact of heart rate, mean arterial pressure and intraocular pressure on flow density in primary open-angle glaucoma patients. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019;97:e844–e9. - PubMed
-
- Verticchio Vercellin AC, Harris A, Tanga L, Siesky B, Quaranta L, Rowe LW, et al. Optic nerve head diurnal vessel density variations in glaucoma and ocular hypertension measured by optical coherence tomography angiography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020;258:1237–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
