Elevated Monocyte-to-High-Density Lipoprotein Ratio as an Indicator of Systemic Inflammation in Patients with Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
- PMID: 35005518
- PMCID: PMC8697051
- DOI: 10.14744/bej.2021.94547
Elevated Monocyte-to-High-Density Lipoprotein Ratio as an Indicator of Systemic Inflammation in Patients with Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
Abstract
Objectives: This study was designed to assess the monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein (HDL) ratio (MHR) as a possible marker of systemic inflammation in patients with branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO).
Methods: A study group of 62 patients with BRVO and a control group of 60 age-matched, healthy individuals were enrolled in the study. The blood lipid profile, hematology profile, and C-reactive protein (CRP) level were measured. The MHR was calculated as the ratio of the monocyte count to the HDL level, and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) was calculated as the ratio of the neutrophil count to the lymphocyte count.
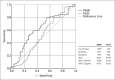
Results: In patients with BRVO versus controls, the mean MHR was 14.1±5.1 vs 12.2±4.3 (p=.032), the mean NLR was 1.99±0.69 vs 2.01±0.86 (p=.889), and the mean CRP level was 3.44±2.53 mg/L vs 2.81±1.57 mg/L (p=.102). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for the MHR and the NLR was 0.621 and 0.519, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of the MHR and the NLR to predict BRVO was 51% and 73% vs 79% and 35%, respectively.
Conclusion: The MHR values were higher in patients with BRVO compared with those of the control group. BRVO seems to be associated with systemic inflammation.
Keywords: Branch retinal vein occlusion; MHR; inflammation; monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio.
Copyright © 2021 by Beyoglu Eye Training and Research Hospital.
Figures
References
-
- Yau JW, Lee P, Wong TY, Best J, Jenkins A. Retinal vein occlusion: An approach to diagnosis, systemic risk factors and management. Intern Med J. 2008;38:904–10. - PubMed
-
- Wong TY, Larsen EK, Klein R, Mitchell P, Couper DJ, Klein BE, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors for retinal vein occlusion and arteriolar emboli: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities & Cardiovascular Health studies. Ophthalmology. 2005;112:540–7. - PubMed
-
- Kesler A, Shalev V, Rogowski O, Shimron O, Shainberg B, Sela BA, et al. Comparative analysis of homocysteine concentrations in patients with retinal vein occlusion versus thrombotic and atherosclerotic disorders. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2008;19:259–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous