Origin and evolutionary analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
- PMID: 35005525
- PMCID: PMC8718870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobb.2021.12.001
Origin and evolutionary analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
Abstract
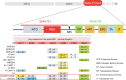
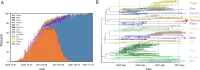
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has evolved rapidly into new variants throughout the pandemic. The Omicron variant has more than 50 mutations when compared with the original wild-type strain and has been identified globally in numerous countries. In this report, we analyzed the mutational profiles of several variants, including the per-site mutation rate, to determine evolutionary relationships. The Omicron variant was found to have a unique mutation profile when compared with that of other SARS-CoV-2 variants, containing mutations that are rare in clinical samples. Moreover, the presence of five mouse-adapted mutation sites suggests that Omicron may have evolved in a mouse host. Mutations in the Omicron receptor-binding domain (RBD) region, in particular, have potential implications for the ongoing pandemic.
Keywords: Mouse-adapted mutation; Omicron variant; Reverse zoonosis; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous Screening of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta Variants Using High-Resolution Melting Analysis.Biol Pharm Bull. 2022 Apr 1;45(4):394-396. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b21-01081. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Biol Pharm Bull. 2022. PMID: 35067489
-
Omicron and Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2: A comparative computational study of spike protein.J Med Virol. 2022 Apr;94(4):1641-1649. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27526. Epub 2021 Dec 27. J Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34914115
-
Genetic differentiation and diversity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in its early outbreak.Biosaf Health. 2022 Jun;4(3):171-178. doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2022.04.004. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Biosaf Health. 2022. PMID: 35496653 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Mutation Is Faster than the Chase: Multiple Mutations on Spike/ACE2 Interaction Residues.Immune Netw. 2021 Dec 23;21(6):e38. doi: 10.4110/in.2021.21.e38. eCollection 2021 Dec. Immune Netw. 2021. PMID: 35036025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2: Mutation, infectivity, transmission, and vaccine resistance.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Jan 7;10(1):1-11. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i1.1. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 35071500 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations and Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein.Viruses. 2022 Mar 19;14(3):640. doi: 10.3390/v14030640. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35337047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Validation of Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for Detecting Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in Cattle, Swine, and Chicken.Viruses. 2022 Jun 22;14(7):1358. doi: 10.3390/v14071358. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35891340 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of vaccine candidate against Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 using immunoinformatic approaches.In Silico Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 26;10(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s40203-022-00128-y. eCollection 2022. In Silico Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35898574 Free PMC article.
-
Variable neutralizing antibody responses to 10 SARS-CoV-2 variants in natural infection with wild- type (B.1) virus, Kappa (B.1.617.1), and Delta (B.1.617.2) variants and COVISHIELD vaccine immunization in India: utility of the MSD platform.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 5;14:1181991. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181991. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37342350 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Networked SARS-CoV-2 Peptides Elicit T Cell Responses with Enhanced Specificity.Immunohorizons. 2023 Jun 1;7(6):508-527. doi: 10.4049/immunohorizons.2300034. Immunohorizons. 2023. PMID: 37358499 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
