Origin and evolutionary analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
- PMID: 35005525
- PMCID: PMC8718870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobb.2021.12.001
Origin and evolutionary analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant
Abstract
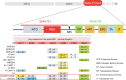
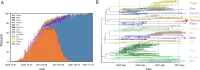
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has evolved rapidly into new variants throughout the pandemic. The Omicron variant has more than 50 mutations when compared with the original wild-type strain and has been identified globally in numerous countries. In this report, we analyzed the mutational profiles of several variants, including the per-site mutation rate, to determine evolutionary relationships. The Omicron variant was found to have a unique mutation profile when compared with that of other SARS-CoV-2 variants, containing mutations that are rare in clinical samples. Moreover, the presence of five mouse-adapted mutation sites suggests that Omicron may have evolved in a mouse host. Mutations in the Omicron receptor-binding domain (RBD) region, in particular, have potential implications for the ongoing pandemic.
Keywords: Mouse-adapted mutation; Omicron variant; Reverse zoonosis; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
