SARS-CoV-2 infection enhances mitochondrial PTP complex activity to perturb cardiac energetics
- PMID: 35005527
- PMCID: PMC8720045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103722
SARS-CoV-2 infection enhances mitochondrial PTP complex activity to perturb cardiac energetics
Abstract
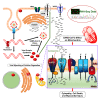
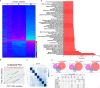
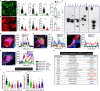
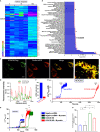
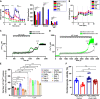
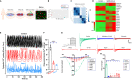
SARS-CoV-2 is a newly identified coronavirus that causes the respiratory disease called coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). With an urgent need for therapeutics, we lack a full understanding of the molecular basis of SARS-CoV-2-induced cellular damage and disease progression. Here, we conducted transcriptomic analysis of human PBMCs, identified significant changes in mitochondrial, ion channel, and protein quality-control gene products. SARS-CoV-2 proteins selectively target cellular organelle compartments, including the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. M-protein, NSP6, ORF3A, ORF9C, and ORF10 bind to mitochondrial PTP complex components cyclophilin D, SPG-7, ANT, ATP synthase, and a previously undescribed CCDC58 (coiled-coil domain containing protein 58). Knockdown of CCDC58 or mPTP blocker cyclosporin A pretreatment enhances mitochondrial Ca2+ retention capacity and bioenergetics. SARS-CoV-2 infection exacerbates cardiomyocyte autophagy and promotes cell death that was suppressed by cyclosporin A treatment. Our findings reveal that SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins suppress cardiomyocyte mitochondrial function that disrupts cardiomyocyte Ca2+ cycling and cell viability.
Keywords: Cardiovascular medicine; Transcriptomics; Virology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alavian K.N., Beutner G., Lazrove E., Sacchetti S., Park H.A., Licznerski P., Li H., Nabili P., Hockensmith K., Graham M., et al. An uncoupling channel within the c-subunit ring of the F1FO ATP synthase is the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2014;111:10580–10585. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bers D.M. Calcium and cardiac rhythms: physiological and pathophysiological. Circ. Res. 2002;90:14–17. - PubMed
-
- Bers D.M. Calcium cycling and signaling in cardiac myocytes. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008;70:23–49. - PubMed
-
- Bers D.M. Cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium leak: basis and roles in cardiac dysfunction. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2014;76:107–127. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

