Synthetic antibacterial discovery of symbah-1, a macrocyclic β-hairpin peptide antibiotic
- PMID: 35005555
- PMCID: PMC8719016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103611
Synthetic antibacterial discovery of symbah-1, a macrocyclic β-hairpin peptide antibiotic
Abstract
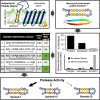
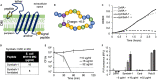
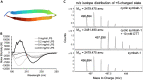
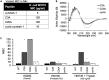
The rapid development and spread of antibiotic resistance necessitate the development of novel strategies for antibiotic discovery. Symbah-1, a synthetic peptide antibiotic, was identified in a high-throughput antibacterial screen of random peptide sequences. Symbah-1 functions through membrane disruption and contains broad spectrum bactericidal activity against several drug-resistant pathogens. Circular dichroism and high-resolution mass spectrometry indicate symbah-1 has a β-hairpin structure induced by lipopolysaccharide and is cyclized via an intramolecular disulfide bond. Together these data classify symbah-1 as an uncommon synthetic member of the β-hairpin antimicrobial peptide class. Symbah-1 displays low hemolysis but loses activity in human serum. Characterization of a symbah-1 peptide library identified two variants with increased serum activity and protease resistance. The method of discovery and subsequent characterization of symbah-1 suggests large synthetic peptide libraries bias toward macrocyclic β-hairpin structure could be designed and screened to rapidly expand and better understand this rare peptide antibiotic class.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Microbiology; Structural biology.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Andolina G., Bencze L.-C., Zerbe K., Müller M., Steinmann J., Kocherla H., Mondal M., Sobek J., Moehle K., Malojčić G., et al. A peptidomimetic antibiotic interacts with the periplasmic Domain of LptD from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018;13:666–675. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00822. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arroyo L.A., Herrera C.M., Fernandez L., Hankins J.V., Trent M.S., Hancock R.E.W. The pmrCAB operon mediates polymyxin resistance in acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978 and clinical isolates through phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011;55:3743–3751. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00256-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S.) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S.); 2019. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

