Immunomodulatory functions of human mesenchymal stromal cells are enhanced when cultured on HEP/COL multilayers supplemented with interferon-gamma
- PMID: 35005599
- PMCID: PMC8715375
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100194
Immunomodulatory functions of human mesenchymal stromal cells are enhanced when cultured on HEP/COL multilayers supplemented with interferon-gamma
Abstract
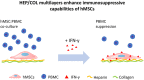
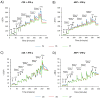
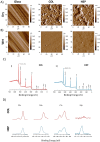
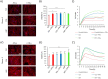
Human mesenchymal stromal cells (hMSCs) are multipotent cells that have been proposed for cell therapies due to their immunosuppressive capacity that can be enhanced in the presence of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). In this study, multilayers of heparin (HEP) and collagen (COL) (HEP/COL) were used as a bioactive surface to enhance the immunomodulatory activity of hMSCs using soluble IFN-γ. Multilayers were formed, via layer-by-layer assembly, varying the final layer between COL and HEP and supplemented with IFN-γ in the culture medium. We evaluated the viability, adhesion, real-time growth, differentiation, and immunomodulatory activity of hMSCs on (HEP/COL) multilayers. HMSCs viability, adhesion, and growth were superior when cultured on (HEP/COL) multilayers compared to tissue culture plastic. We also confirmed that hMSCs osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation remained unaffected when cultured in (HEP/COL) multilayers in the presence of IFN-γ. We measured the immunomodulatory activity of hMSCs by measuring the level of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) expression. IDO expression was higher on (HEP/COL) multilayers treated with IFN-γ. Lastly, we evaluated the suppression of peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) proliferation when co-cultured with hMSCs on (HEP/COL) multilayers with IFN-γ. hMSCs cultured in (HEP/COL) multilayers in the presence of soluble IFN-γ have a greater capacity to suppress PBMC proliferation. Altogether, (HEP/COL) multilayers with IFN-γ in culture medium provides a potent means of enhancing and sustaining immunomodulatory activity to control hMSCs immunomodulation.
Keywords: Collagen; Heparin; Human mesenchymal stromal cells; Interferon gamma; Layer-by-Layer.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

