Synergistic effect of microwave heating and hydrothermal treatment on cyanogenic glycosides and bioactive compounds of plum (Prunus domestica L.) kernels: An analytical approach
- PMID: 35005633
- PMCID: PMC8717145
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2021.12.007
Synergistic effect of microwave heating and hydrothermal treatment on cyanogenic glycosides and bioactive compounds of plum (Prunus domestica L.) kernels: An analytical approach
Abstract
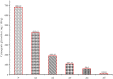
The effects of microwave heating (450 W for 6 min), hydrothermal treatment (6, 9, and 12 h at 45 °C) and their combination on compositional characteristics, cyanogenic glycosides, color, and bioactive compounds of plum kernels have been studied. The conditions examined caused a significant reduction of 37.81, 72.17, 84.41, 91.24 and 98.02% in cyanogenic glycosides of differently treated plum kernels. Total phenolic and total flavonoid compounds of plum kernels showed hydrothermal time-dependent duration decline. The larger shifts in FT-IR spectra near 1157 cm-1 provided valuable insights on the reduction of cyanogenic glycosides during combined treatments. The variation of color attributes (L*, a*, b*), during combined treatments indicates a more reddish tonality of plum kernel samples. The combined effect of hydrothermal (12 h at 45 °C) and microwave heating (450 W for 6 min) proved to be an effective tool for neutralizing the toxic effect of cyanogenic glycosides, opening up possibilities for its use in food industries.
Keywords: Bioactive compounds; Cyanogenic glycosides; Detoxification; FT-IR; Plum kernels.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- AOAC . seventeenth ed. The Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Gaithersburg, MD, USA: 2000. Official Methods of Analysis. Methods, 950.01, 920.39, 945.01, 985.29, and 942.05.
-
- Bolarinwa I.F., Orfila C., Morgan M.R. Amygdalin content of seeds, kernels, and food products commercially available in the UK. Food Chem. 2014;152:133–139. - PubMed
-
- Chavez-Murillo C.E., Veyna-Torres J.I., Cavazos-Tamez L.M., de la Rosa-Millan J., Serna-Saldivar S.O. Physicochemical characteristics, ATR-FTIR molecular interactions and in vitro starch and protein digestion of thermally treated whole pulse flours. Food Res. Int. 2018;105:371–383. - PubMed
-
- Divekar M.T., Karunakaran C., Lahlali R., Kumar S., Chelladurai V., Liu X., Borondics F., Shanmugasundaram S., Jayas D.S. Effect of microwave treatment on the cooking and macronutrient qualities of pulses. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017;20:409–422.
-
- Dulf F.V., Vodnar D.C., Socaciu C. Effects of solid-state fermentation with two filamentous fungi on the total phenolic contents, flavonoids, antioxidant activities and lipid fractions of plum fruit (Prunus domestica L.) by-products. Food Chem. 2016;209:27–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

