Microbe mediated remediation of dyes, explosive waste and polyaromatic hydrocarbons, pesticides and pharmaceuticals
- PMID: 35005657
- PMCID: PMC8717453
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2021.100092
Microbe mediated remediation of dyes, explosive waste and polyaromatic hydrocarbons, pesticides and pharmaceuticals
Abstract
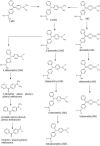
Industrialization and human activities have led to serious effects on environment. With the progress taking place in the biodegradation field, it is important to summarize the latest advancement. In this review, we intend to provide insights on the recent progress on the biodegradation of environmental contaminants such as dyes, pesticides, pharmaceuticals, explosive waste and polyaromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. Along with the biodegradation of environmental contaminants, toxicity effects have also been discussed.
Keywords: Biodegradation; Dyes; Explosive waste; Microbes; PAHs; Pesticides; Pharmaceuticals.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Figures




References
-
- Abdel-Shafy H.I., Mansour M.S. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016;25(1):107–123.
-
- Abe F.R., Soares A.M., de Oliveira D.P., Gravato C. Toxicity of dyes to zebrafish at the biochemical level: cellular energy allocation and neurotoxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2018;235:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Acuña A.J., Pucci O.H., Pucci G.N. InTech New Tech Oil Gas Ind. 2012. Electrobioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil from Patagonia Argentina; pp. 29–48.
-
- Agrawal S., Tipre D., Patel B., Dave S. Optimization of triazo Acid Black 210 dye degradation by Providencia sp. SRS82 and elucidation of degradation pathway. Process Biochem. 2014;49(1):110–119.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

