Graphene nanostructures for input-output bioelectronics
- PMID: 35005709
- PMCID: PMC8717360
- DOI: 10.1063/5.0073870
Graphene nanostructures for input-output bioelectronics
Abstract
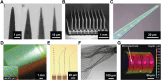
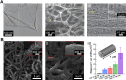
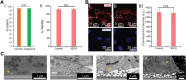
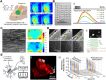
The ability to manipulate the electrophysiology of electrically active cells and tissues has enabled a deeper understanding of healthy and diseased tissue states. This has primarily been achieved via input/output (I/O) bioelectronics that interface engineered materials with biological entities. Stable long-term application of conventional I/O bioelectronics advances as materials and processing techniques develop. Recent advancements have facilitated the development of graphene-based I/O bioelectronics with a wide variety of functional characteristics. Engineering the structural, physical, and chemical properties of graphene nanostructures and integration with modern microelectronics have enabled breakthrough high-density electrophysiological investigations. Here, we review recent advancements in 2D and 3D graphene-based I/O bioelectronics and highlight electrophysiological studies facilitated by these emerging platforms. Challenges and present potential breakthroughs that can be addressed via graphene bioelectronics are discussed. We emphasize the need for a multidisciplinary approach across materials science, micro-fabrication, and bioengineering to develop the next generation of I/O bioelectronics.
© 2021 Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
