Protein Removal from Hydrogels through Repetitive Surface Degradation
- PMID: 35005931
- PMCID: PMC8693177
- DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.1c00993
Protein Removal from Hydrogels through Repetitive Surface Degradation
Abstract
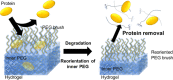
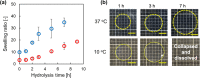
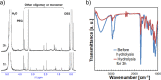
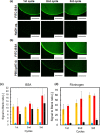
Suppression of protein adsorption is a necessary property for materials used in the living body. In this study, thermoresponsive and degradable hydrogels were prepared by the radical polymerization of 2-methylene-1,3-dioxepane, 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA), and poly(ethylene glycol) monomethacrylate (PEGMA). The prepared hydrogels re-exposed PEG-grafted chains to the interface through surface degradation, which was confirmed by the maintenance of the chemical composition of the hydrogel surfaces after hydrolysis. Notably, adsorbed proteins can be removed from the hydrogel surfaces through hydrogel surface degradation at least thrice.
Keywords: 2-methylene-1,3-dioxepane; degradation; hydrogel surface; hydrogels; protein removable surface; thermoresponsive.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thermoresponsive degradable hydrogels with renewable surfaces for protein removal.Biomater Sci. 2024 Dec 17;13(1):324-329. doi: 10.1039/d4bm01383b. Biomater Sci. 2024. PMID: 39584771
-
Gelation characteristics and osteogenic differentiation of stromal cells in inert hydrolytically degradable micellar polyethylene glycol hydrogels.Biomacromolecules. 2012 Jul 9;13(7):2073-86. doi: 10.1021/bm300453k. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Biomacromolecules. 2012. PMID: 22642902
-
Biodegradation of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) and poly{(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)-co-[poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate]} hydrogels containing peptide-based cross-linking agents.Biomacromolecules. 2010 Nov 8;11(11):2949-59. doi: 10.1021/bm100756c. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Biomacromolecules. 2010. PMID: 20961104
-
The impact of functional groups of poly(ethylene glycol) macromers on the physical properties of photo-polymerized hydrogels and the local inflammatory response in the host.Acta Biomater. 2018 Feb;67:42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.12.007. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29242160 Free PMC article.
-
Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for biomedical applications.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014 Nov;88(3):575-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.07.005. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014. PMID: 25092423 Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation of Degradable and Transformable Core-Corona-Type Particles that Control Cellular Uptake by Thermal Shape Change.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024 Feb 12;10(2):897-904. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c01554. Epub 2024 Jan 20. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 38243792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tamada Y.; Ikada Y. Effect of Preadsorbed Proteins on Cell Adhesion to Polymer Surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 155, 334–339. 10.1006/jcis.1993.1044. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

