Score for the Risk and Overall Survival of Lung Metastasis in Patients First Diagnosed With Soft Tissue Sarcoma: A Novel Nomogram-Based Risk Assessment System
- PMID: 35006028
- PMCID: PMC8753250
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338211066240
Score for the Risk and Overall Survival of Lung Metastasis in Patients First Diagnosed With Soft Tissue Sarcoma: A Novel Nomogram-Based Risk Assessment System
Abstract
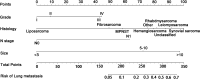
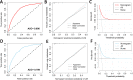
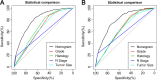
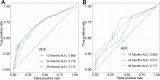
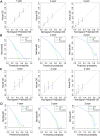
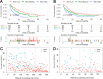
Background: Metastatic soft tissue sarcoma (STS) patients have a poor prognosis with a 3-year survival rate of 25%. About 30% of them present lung metastases (LM). This study aimed to construct 2 nomograms to predict the risk of LM and overall survival of STS patients with LM. Materials and Methods: The data of patients were derived from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database during the period of 2010 to 2015. Logistic and Cox analysis was performed to determine the independent risk factors and prognostic factors of STS patients with LM, respectively. Afterward, 2 nomograms were, respectively, established based on these factors. The performance of the developed nomogram was evaluated with receiver operating characteristic curves, area under the curve (AUC) calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA). Results: A total of 7643 patients with STS were included in this study. The independent predictors of LM in first-diagnosed STS patients were N stage, grade, histologic type, and tumor size. The independent prognostic factors for STS patients with LM were age, N stage, surgery, and chemotherapy. The AUCs of the diagnostic nomogram were 0.806 in the training set and 0.799 in the testing set. For the prognostic nomogram, the time-dependent AUC values of the training and testing set suggested a favorable performance and discrimination of the nomogram. The 1-, 2-, and 3-year AUC values were 0.698, 0.718, and 0.715 in the training set, and 0.669, 0.612, and 0717 in the testing set, respectively. Furthermore, for the 2 nomograms, calibration curves indicated satisfactory agreement between prediction and actual survival, and DCA indicated its clinical usefulness. Conclusion: In this study, grade, histology, N stage, and tumor size were identified as independent risk factors of LM in STS patients, age, chemotherapy surgery, and N stage were identified as independent prognostic factors of STS patients with LM, these developed nomograms may be an effective tool for accurately predicting the risk and prognosis of newly diagnosed patients with LM.
Keywords: Cox regression analysis; Epidemiology; Surveillance; and End Results; logistics regression analysis; nomogram; soft tissue functionality; surgeries.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early distinction of lymph node metastasis in patients with soft tissue sarcoma and individualized survival prediction using the online available nomograms: A population-based analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 7;12:959804. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.959804. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36568161 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of Novel Nomograms for Predicting Specific Distant Metastatic Sites and Overall Survival of Patients With Soft Tissue Sarcoma.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:1533033821997828. doi: 10.1177/1533033821997828. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 33706618 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic nomograms for laryngeal carcinoma patients with lung metastasis: a SEER-based study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Jun;281(6):3071-3082. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08608-x. Epub 2024 Apr 7. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38584217
-
A New Online Dynamic Nomogram: Construction and Validation of a Predictive Model for Distant Metastasis Risk and Prognosis in Patients with Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors.J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 Jul;27(7):1429-1444. doi: 10.1007/s11605-023-05706-9. Epub 2023 May 25. J Gastrointest Surg. 2023. PMID: 37231240 Review.
-
Predictors of Distant Metastasis and Prognosis in Newly Diagnosed T1 Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Jan 17;2023:6638755. doi: 10.1155/2023/6638755. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36704724 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Medical Use of Fullerenols After Two Decades of Oncology Research.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231201515. doi: 10.1177/15330338231201515. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37724005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feasibility and therapeutic potential of [177Lu]Lu-FAPI-2286 in patients with advanced metastatic sarcoma.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Dec;52(1):237-246. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06795-7. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39060377 Clinical Trial.
-
A novel nomogram and prognostic factor for metastatic soft tissue sarcoma survival.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 13;15:1371910. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1371910. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38803474 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors of Early Distant Metastasis After Primary Tumor Treatment in Soft Tissue Sarcoma.In Vivo. 2022 Sep-Oct;36(5):2260-2264. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12954. In Vivo. 2022. PMID: 36099122 Free PMC article.
-
Early distinction of lymph node metastasis in patients with soft tissue sarcoma and individualized survival prediction using the online available nomograms: A population-based analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 7;12:959804. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.959804. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36568161 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

