G-protein coupled receptor, PI3K and Rho signaling pathways regulate the cascades of Tau and amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 35006431
- PMCID: PMC8607389
- DOI: 10.1186/s43556-021-00036-1
G-protein coupled receptor, PI3K and Rho signaling pathways regulate the cascades of Tau and amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
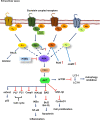
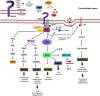
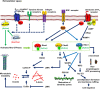
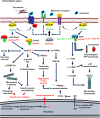
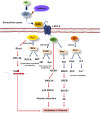
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease characterized by the presence of amyloid-β plaques in the extracellular environment and aggregates of Tau protein that forms neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in neuronal cells. Along with these pathological proteins, the disease shows neuroinflammation, neuronal death, impairment in the immune function of microglia and synaptic loss, which are mediated by several important signaling pathways. The PI3K/Akt-mediated survival-signaling pathway is activated by many receptors such as G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2), and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor. The signaling pathway not only increases the survival of neurons but also regulates inflammation, phagocytosis, cellular protection, Tau phosphorylation and Aβ secretion as well. In this review, we focused on receptors, which activate PI3K/Akt pathway and its potential to treat Alzheimer's disease. Among several membrane receptors, GPCRs are the major drug targets for therapy, and GPCR signaling pathways are altered during Alzheimer's disease. Several GPCRs are involved in the pathogenic progression, phosphorylation of Tau protein by activation of various cellular kinases and are involved in the amyloidogenic pathway of amyloid-β synthesis. Apart from various GPCR signaling pathways, GPCR regulating/ interacting proteins are involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. These include several small GTPases, Ras homolog enriched in brain, GPCR associated sorting proteins, β-arrestins, etc., that play a critical role in disease progression and has been elaborated in this review.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; GPCR; LPA; PI3K/Akt; Rho GTPase; TREM2; Tau.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cvetković-Dožić D, Skender-Gazibara M, Dožić S. Neuropathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Oncol. 2001;9(3):195–199.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
