Systematic review of risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and severity of COVID-19 with therapies approved to treat multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 35006442
- PMCID: PMC8743352
- DOI: 10.1007/s10072-021-05846-3
Systematic review of risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and severity of COVID-19 with therapies approved to treat multiple sclerosis
Abstract
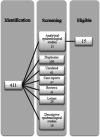
There is growing concern that multiple sclerosis (MS) patients on certain therapies may be at higher risk for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We conducted a systematic literature review to examine the available data on U.S. therapies approved to treat MS and the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe COVID-19 outcomes. We conducted searches in PubMed, Embase, and the WHO COVID-19 database through May 2, 2021, and retrieved articles describing clinical data on therapies approved to treat MS and the risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2 or the effects of such therapies on clinical outcomes of COVID-19. The literature search identified a total of 411 articles: 97 in PubMed, 227 in Embase, and 87 in the WHO database. After excluding duplicates and screening, we identified 15 articles of interest. We identified an additional article through a broader secondary weekly search in PubMed. Thus, ultimately, we reviewed 16 observational studies. Available data, which suggest that MS patients treated with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies may be at increased risk for severe COVID-19, are subject to relevant limitations. Generally, studies did not identify increased risk for COVID-19 worsening with other therapies approved to treat MS. Based on observational data, biological plausibility, novelty of the drug-event association, and public health implications in a subpopulation with potential impaired response to the COVID-19 vaccines, this safety signal merits further monitoring.
Keywords: Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody; COVID-19; Immunomodulatory therapies; Immunosuppressive therapies; Multiple sclerosis; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022. This is a U.S. government work and not under copyright protection in the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2021) COVID-19: People with certain medical conditions. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-.... Accessed 26 May 2021
-
- Laroni A et al (2020) COVID-19 in patients with multiple sclerosis undergoing disease-modifying treatments. Mult Scler 27(14):2126–2136. 10.1177/1352458520971817 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous