Etodolac improves collagen induced rheumatoid arthritis in rats by inhibiting synovial inflammation, fibrosis and hyperplasia
- PMID: 35006449
- PMCID: PMC8607370
- DOI: 10.1186/s43556-021-00052-1
Etodolac improves collagen induced rheumatoid arthritis in rats by inhibiting synovial inflammation, fibrosis and hyperplasia
Abstract
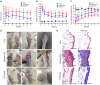
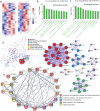
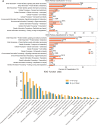
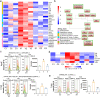
Synovial hyperplasia is the main cause of chronic rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but the mechanism of synovial hyperplasia is still unclear. Etodolac (ETD) is a selective COX-2 inhibitor for relieving pain and stiffness in RA, but the disease modifying effect is still lack of evidence. Proteomics method was used to study the differential proteome of synovial tissue in collagen induced arthritis (CIA) in rats. With the help of STRING analysis, the upregulated proteins enriched in the cluster of complement and coagulation cascades and platelet degranulation were highlighted, these proteins with fibrogenic factors Lum, CIV, CXI and Tgfbi participated in the synovial inflammation, fibrosis and hyperplasia in CIA. Based on KOG function class analysis, the proteins involved in the events of the central dogma was explored. They might be hyperplasia related proteins for most of them are related to the proliferation of cancer. ETD significantly attenuated synovial inflammation, fibrosis and hyperplasia in CIA rats by downregulating these proteins. Several proteins have not been observed in RA so far, such as Tmsb4x, Pura, Nfic, Ruvbl1, Snrpd3, U2af2, Srrm2, Srsf7, Elavl1, Hnrnph1, Wars, Yars, Bzw2, Mcts1, Eif4b, Ctsh, Lamp1, Dpp7, Ptges3, Cdc37 and Septin9, they might be potentials targets for RA. Blood biochemistry tests showed the safety of 7 months use of ETD on rats. In conclusion, present study displayed a comprehensive mechanism of synovial hyperplasia in CIA rats, on this basis, the clinical value of ETD in the treatment of RA was well confirmed.
Keywords: Etodolac; Proteomics; Rheumatoid arthritis; Synovial hyperplasia.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors of this paper are employees of Lunan Pharmaceutical Group, the research funds are provided by Lunan pharmaceutical Group.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Traditional Chinese medicine formula Bi-Qi capsule alleviates rheumatoid arthritis-induced inflammation, synovial hyperplasia, and cartilage destruction in rats.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Mar 14;20(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1547-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29540195 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of synovial hyperplasia, angiogenesis and osteoclastogenesis in the protective effect of apigenin on collagen-induced arthritis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Aug;73:362-369. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.05.024. Epub 2019 May 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31132731
-
Sigesbeckia orientalis L. Extract Alleviated the Collagen Type II-Induced Arthritis Through Inhibiting Multi-Target-Mediated Synovial Hyperplasia and Inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 28;11:547913. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.547913. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32982752 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in focal adhesion kinase expression in rats with collagen-induced arthritis and efficacy of intervention with disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs alone or in combination.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Dec 1;8(12):15573-81. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26884826 Free PMC article.
-
[Rheumatoid arthritis: new developments in the pathogenesis with special reference to synovial fibroblasts].Z Rheumatol. 2001 Oct;60(5):309-18. doi: 10.1007/s003930170030. Z Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11759230 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Follicular mediated etodolac phosalosomal gel for contact dermatitis alleviation, insights from optimization to in-vivo appraisal.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 18;14(1):21744. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71456-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39289408 Free PMC article.
-
hnRNPH1: A Multifaceted Regulator in RNA Processing and Disease Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 28;26(11):5159. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115159. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural medicines of targeted rheumatoid arthritis and its action mechanism.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 1;13:945129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.945129. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35979373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of two potential immune-related biomarkers of Graves' disease based on integrated bioinformatics analyses.Endocrine. 2022 Nov;78(2):306-314. doi: 10.1007/s12020-022-03156-y. Epub 2022 Aug 13. Endocrine. 2022. PMID: 35962894
-
Biological Activities of Etodolac-Based Hydrazone, Thiazolidinone and Triazole Derivatives on Breast Cancer Cell Lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025 Aug;39(8):e70428. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70428. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40787711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Fry-Smith A, Harris G, Taylor RS. Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2008;12(11):1–iii. doi: 10.3310/hta12110. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dvornik DM. Tissue selective inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis by etodolac. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1997;47:40–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
