Heavy metal-induced stress in eukaryotic algae-mechanisms of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance with particular emphasis on oxidative stress in exposed cells and the role of antioxidant response
- PMID: 35006558
- PMCID: PMC8873139
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-18419-w
Heavy metal-induced stress in eukaryotic algae-mechanisms of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance with particular emphasis on oxidative stress in exposed cells and the role of antioxidant response
Abstract
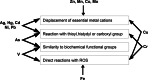
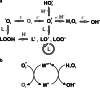
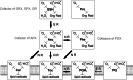
Heavy metals is a collective term describing metals and metalloids with a density higher than 5 g/cm3. Some of them are essential micronutrients; others do not play a positive role in living organisms. Increased anthropogenic emissions of heavy metal ions pose a serious threat to water and land ecosystems. The mechanism of heavy metal toxicity predominantly depends on (1) their high affinity to thiol groups, (2) spatial similarity to biochemical functional groups, (3) competition with essential metal cations, (4) and induction of oxidative stress. The antioxidant response is therefore crucial for providing tolerance to heavy metal-induced stress. This review aims to summarize the knowledge of heavy metal toxicity, oxidative stress and antioxidant response in eukaryotic algae. Types of ROS, their formation sites in photosynthetic cells, and the damage they cause to the cellular components are described at the beginning. Furthermore, heavy metals are characterized in more detail, including their chemical properties, roles they play in living cells, sources of contamination, biochemical mechanisms of toxicity, and stress symptoms. The following subchapters contain the description of low-molecular-weight antioxidants and ROS-detoxifying enzymes, their properties, cellular localization, and the occurrence in algae belonging to different clades, as well as the summary of the results of the experiments concerning antioxidant response in heavy metal-treated eukaryotic algae. Other mechanisms providing tolerance to metal ions are briefly outlined at the end.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; Eukaryotic algae; Heavy metals; Low-molecular-weight antioxidants; Oxidative stress; Toxicity mechanisms.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures
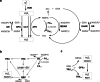

References
-
- Ackova DG. Heavy metals and their general toxicity on plants. Plant Sci Today. 2018;5:15–19. doi: 10.14719/pst.2018.5.1.355. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

